Презентация на тему: Project activity of students as a way of forming productive learning skills


A product of the students’ activity A product of the students’ activity A creative collective, pair, group, individual practical activity of students A way of learning and using foreign language A way of communication

Creation the motivational situation for forming and improving language skills while solving the problematical tasks Creation the motivational situation for forming and improving language skills while solving the problematical tasks Forming Sts’ language and speech skills Stimulation Sts’ language and speech skills Forming articulation and intonation speech skills during the presentation of project

Forming Sts’ sociocultural and sociolingual competences Forming Sts’ sociocultural and sociolingual competences Integrating Sts’ knowledge of foreign languages and other branches of sciences Stimulation the individual creative activity while choosing and making the “project product”

Teacher’s and students’ motivation Teacher’s and students’ motivation Competence



1) planning students’ activity; 1) planning students’ activity; 2) combination of individual and collective activity; 3) organization of collective and interpersonal communication, mutual help, support; 4) using the system of educational methods; 5) directing the students’ activity to making practically meaningful product; 6) creation the situations of success for students.


research project; research project; searching project; creative project; role or game project; practical project

Practical project Practical project





internal (projects, organized in one school, or between schools, by classes in a region, country) internal (projects, organized in one school, or between schools, by classes in a region, country) international (the representatives of different countries take part, for their realization facilities of information technologies can be used)

personal personal pair group

short-range (a few lessons from the program of one subject) short-range (a few lessons from the program of one subject) projects of middle duration (from a week to the month) projects of long duration (a few months)

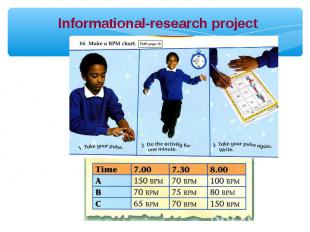
Informational-research projects; Informational-research projects; projects-reviews; production projects; organizational-game projects.




projects, when only a teacher determines their subject, form of implementation and necessary materials; projects, when only a teacher determines their subject, form of implementation and necessary materials; projects, when in the choice of subject, planning and organization of work, a teacher and students take part equally; projects, when only students determine all aspects of work.

1. Problematical character. 1. Problematical character. 2. Variability. 3. Cognitivity. 4. A presence of interest to the educational process. 5. Personal factor. 6. Adaptability.

interests of students as basic criterion interests of students as basic criterion practical application; age and individual features of students; creation of possibility for the independent pulling out and realization the new ideas; accordance to the programme tasks; level of knowledge and abilities of students; volume of works (term of making); account of time, necessary for making the planned project; material and technical base of school cabinet; financial charges (cost of materials); creative character, originality; teacher’s preparation.

1. Choosing the project topic, title and possible problem 1. Choosing the project topic, title and possible problem 2. Choosing the project type 3. Working out the plan 4. Guidance and control 5. Discussing the results

The task here is to bring forward the problem fields which can motivate a student The task here is to bring forward the problem fields which can motivate a student

Teacher’s participation in plan development depends on Sts’ motivation. Teacher’s participation in plan development depends on Sts’ motivation. The teacher should make sure all the Sts understand the topic of the project and the problem they’re supposed to solve. The plan can be drawn individually and then shared with class or guided by the teacher.

Project method is the way to give Sts more freedom and independence in their studies: they choose what, when and where to do. Project method is the way to give Sts more freedom and independence in their studies: they choose what, when and where to do. Leaving a project without guidance might discourage low-motivated Sts. Moreover, group work should be controlled to avoid one person carrying out the whole project alone.

What have you achieved this week? What have you achieved this week? What do you find most difficult at the moment? What questions would you like me to ask? What help do you need? How can you divide the task into simpler ones? What did you fail to do? What result are you trying to achieve by doing it?

A project is a successful way to apply knowledge in real life context. A project is a successful way to apply knowledge in real life context. A teacher should receive an oral or written feedback on project work from every student. A good idea is for a teacher to write the feedback to Sts – to enjoy the next project together!

Step I: Choosing a subject. Step I: Choosing a subject. Step II: Determining the final outcome. Step III: Structuring the project. Step IV: Identifying language skills and strategies. Step V: Gathering the information. Step VI: Compiling and analysing information. Step VII: Presenting the final product. Step VIII: Evaluating the project.