Презентация на тему: Economic Growth

McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.

Economic Growth Increase in real GDP or real GDP per capita over some time periodPercentage rate of growthGrowth as a goalArithmetic of growth: Rule of 70 Approximatenumber of yearsrequired to doublereal GDP = 70 annual percentage rateof growth LO1 25-*

Economic Growth Growth in U.S. real GDP 1950-2009Increased 6 fold 3.2% per year Growth in U.S. real GDP per capitaIncreased more than 3 fold2% per yearQualifications Improved products and servicesAdded leisureOther impacts LO1 25-*

Modern Economic Growth Began with the Industrial Revolution in late 1700sOngoing increases in living standardsTime for leisureSocial changeDemocracyHuman lifespan doubled LO2 25-*

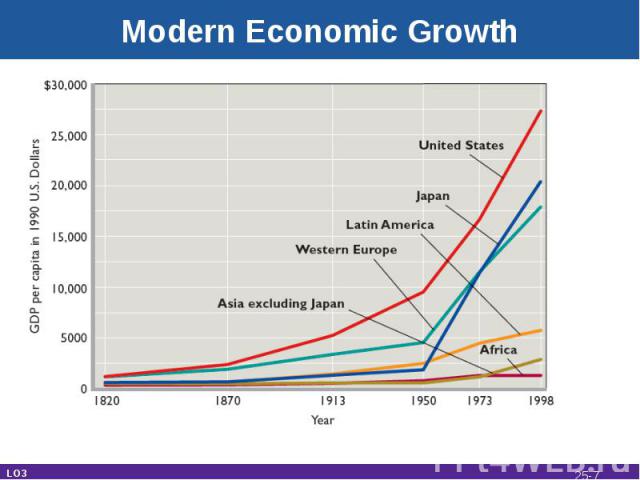
Modern Economic Growth Began in BritainHas spread slowlyStarting date main cause of worldwide differences in living standardsCatching up is possibleLeader countries invent technologyFollower countries adopt technologyCan grow faster LO2 25-*
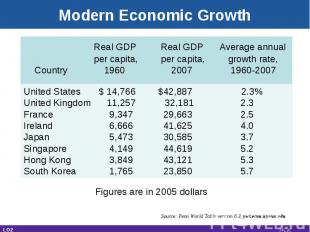
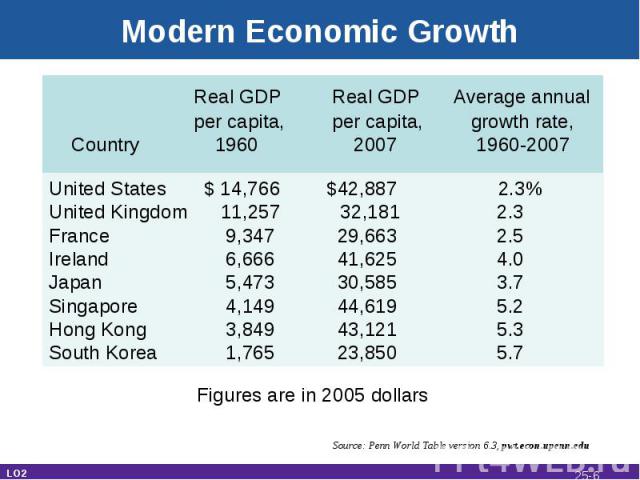
Modern Economic Growth Real GDP Real GDP Average annual per capita, per capita, growth rate, Country 1960 2007 1960-2007 United States $ 14,766 $42,887 2.3%United Kingdom 11,257 32,181 2.3France 9,347 29,663 2.5Ireland 6,666 41,625 4.0Japan 5,473 30,585 3.7Singapore 4,149 44,619 5.2Hong Kong 3,849 43,121 5.3South Korea 1,765 23,850 5.7 Figures are in 2005 dollars Source: Penn World Table version 6.3, pwt.econ.upenn.edu LO2 25-*
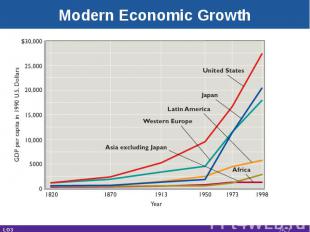
Modern Economic Growth LO3 25-*

Institutional Structures of Growth Strong property rightsPatents and copyrightsEfficient financial institutionsLiteracy and widespread educationFree tradeCompetitive market system LO3 25-*

Determinants of Growth LO3 Supply factors Increases in quantity and quality of natural resources Increases in quality and quantity of human resources Increases in the supply (or stock) of capital goods Improvements in technology Demand factor Households, businesses, and government must purchase the economy’s expanding output Efficiency factor Must achieve economic efficiency and full employment 25-*

Accounting for Growth Factors affecting productivity growthTechnological advance (40%)Quantity of capital (30%)Education and training (15%)Economies of scale and resource allocation (15%) LO3 25-*
Productivity Growth Average rate of growth1.5% per year 1973-19952.8% per year 1995-2009Affects real output, real income, and real wagesPay higher wages without lowering profit LO4 25-*

Productivity Growth Microchip/information technologyNew firms and increasing returnsSources of increasing returnsMore specialized inputsSpreading of development costsSimultaneous consumptionNetwork effectsLearning by doingGlobal competition LO4 25-*

Economic Growth Is economic growth desirable and sustainable?The antigrowth viewEnvironmental and resource issuesIn defense of economic growthHigher standard of livingHuman imagination can solve environmental and resource issues LO5 25-*

Economic Growth Growth is the path to greater material abundanceResults in higher standards of livingIncreases leisure timeAllows for the expansion and application of human knowledge LO5 25-*

Global Perspective LO5 25-*