Презентация на тему: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply

Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply 29 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.

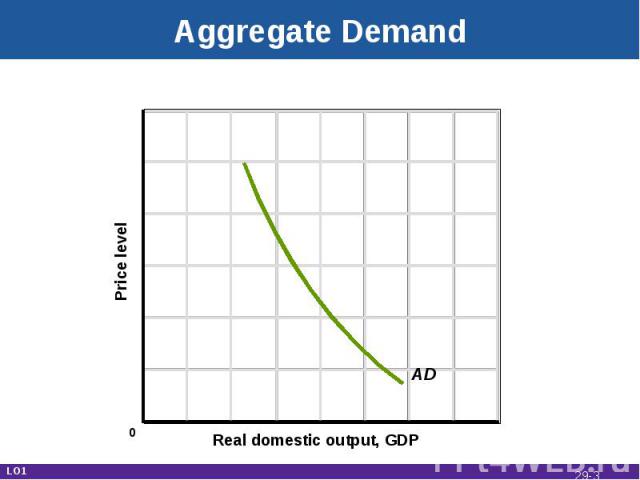
Aggregate Demand Real GDP desired at each price levelInverse relationshipReal balances effectInterest effectForeign purchases effect LO1 29-*
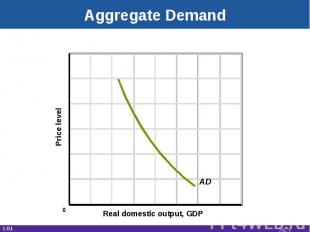
Aggregate Demand Real domestic output, GDP Price level AD LO1 0 29-*
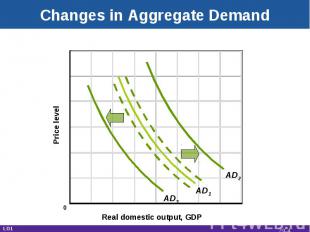
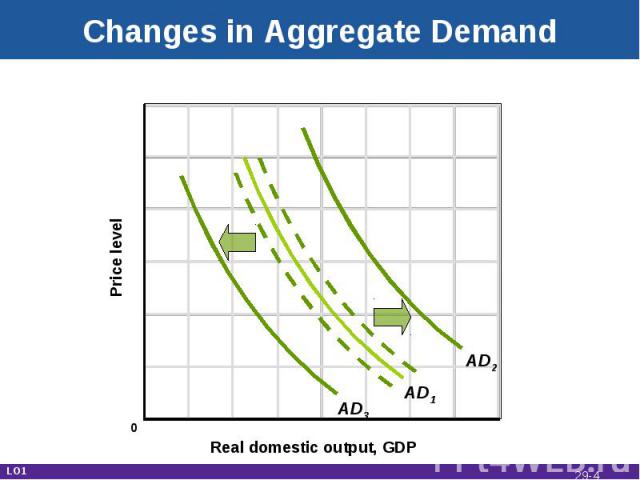
Changes in Aggregate Demand Real domestic output, GDP Price level AD1 AD3 AD2 LO1 0 29-*

Consumer Spending Consumer wealthHousehold borrowingConsumer expectationsPersonal taxes LO1 29-*

Investment Spending Real interest ratesExpected returnsExpectations about future business conditionsTechnologyDegree of excess capacityBusiness taxes LO1 29-*

Government Spending Government spending increasesAggregate demand increases (as long as interest rates and tax rates do not change)More transportation projectsGovernment spending decreasesAggregate demand decreasesLess military spending LO1 29-*

Net Export Spending National income abroadExchange ratesDollar depreciationDollar appreciation LO1 29-*

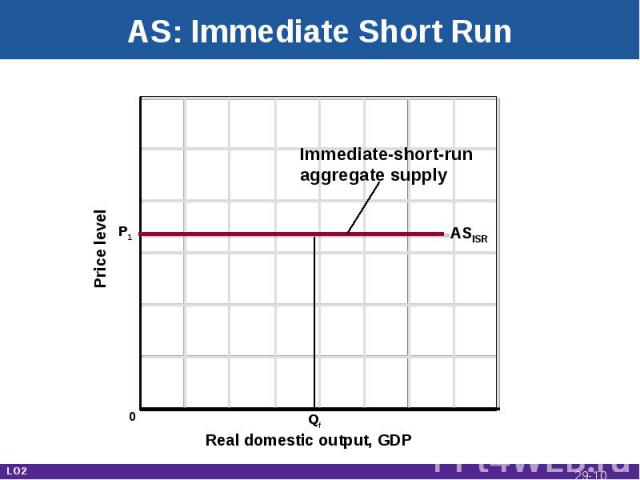
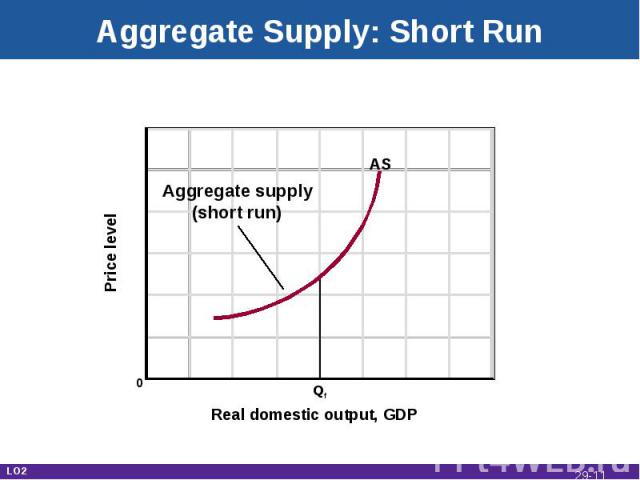
Aggregate Supply Total real output produced at each price levelRelationship depends on time horizonImmediate short runShort runLong run LO2 29-*
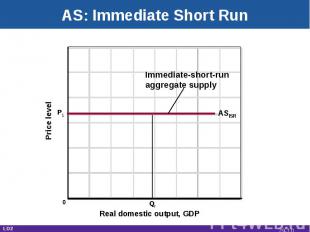
AS: Immediate Short Run Real domestic output, GDP Price level ASISR Qf Immediate-short-runaggregate supply P1 0 LO2 29-*
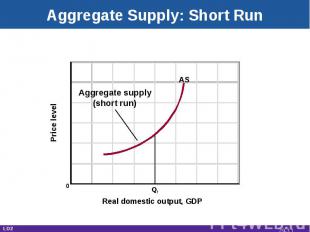
Aggregate Supply: Short Run Real domestic output, GDP Price level 0 Qf AS Aggregate supply(short run) LO2 29-*
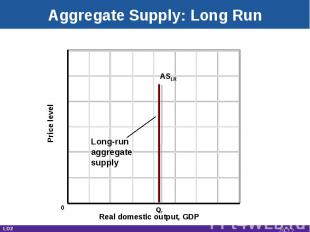
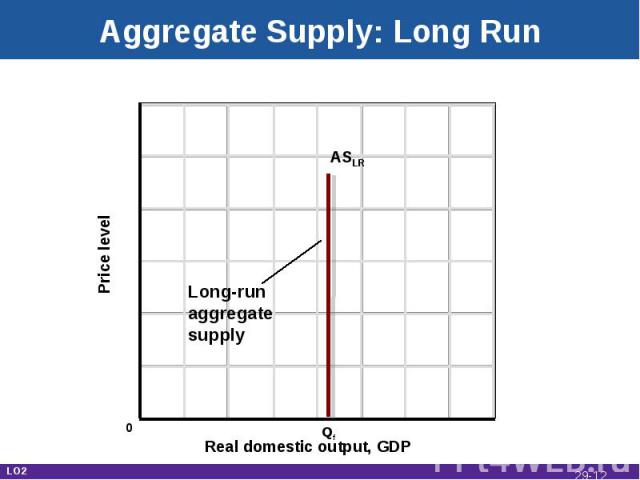
Aggregate Supply: Long Run Real domestic output, GDP Price level ASLR Qf 0 Long-runaggregatesupply LO2 29-*

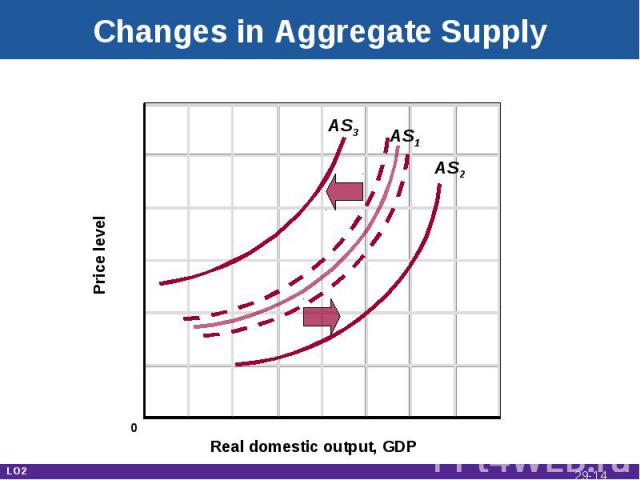
Changes in Aggregate Supply Determinants of aggregate supplyShift factorsCollectively position the AS curveChanges raise or lower per-unit production costs LO2 29-*
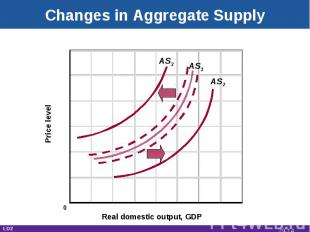
Changes in Aggregate Supply Real domestic output, GDP Price level AS1 AS3 AS2 0 LO2 29-*

Input Prices Domestic resource pricesLaborCapitalLandPrices of imported resourcesImported oilExchange rates LO2 29-*

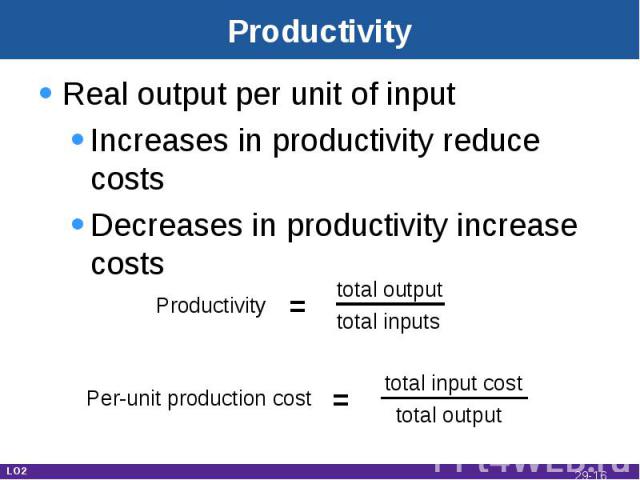
Productivity Real output per unit of inputIncreases in productivity reduce costsDecreases in productivity increase costs LO2 Per-unit production cost = total input cost total output Productivity = total output total inputs 29-*

Legal-Institutional Environment Legal changes alter per-unit costs of outputTaxes and subsidiesExtent of government regulation LO2 29-*
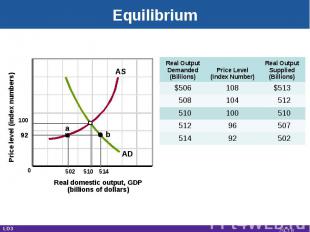
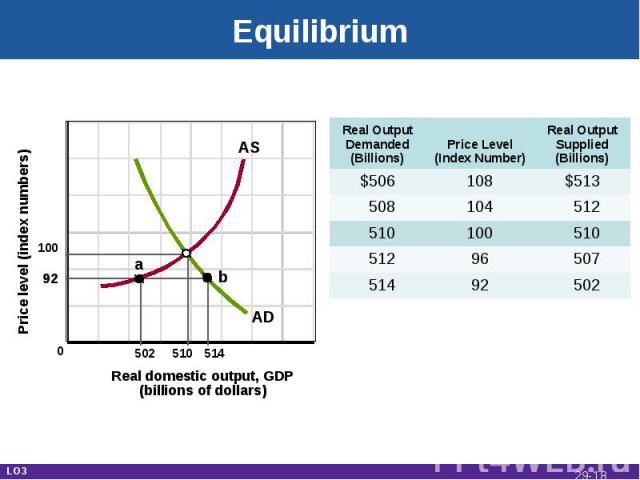
Equilibrium Real domestic output, GDP(billions of dollars) Price level (index numbers) 10092 502 510 514 a b AD AS Real Output Demanded(Billions) Price Level(Index Number) Real OutputSupplied(Billions) $506 108 $513 508 104 512 510 100 510 512 96 507 514 92 502 0 LO3 29-*
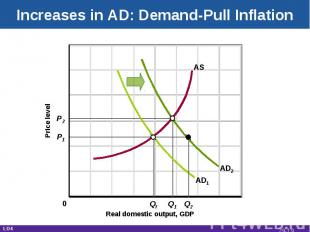
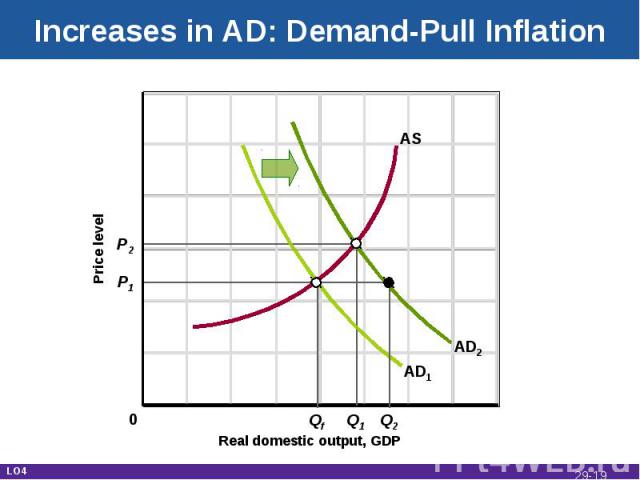
Increases in AD: Demand-Pull Inflation Real domestic output, GDP Price level AD1 AS P1 P2 Q2 Q1 Qf AD2 0 LO4 29-*
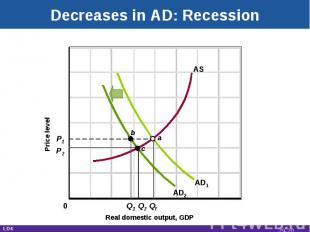
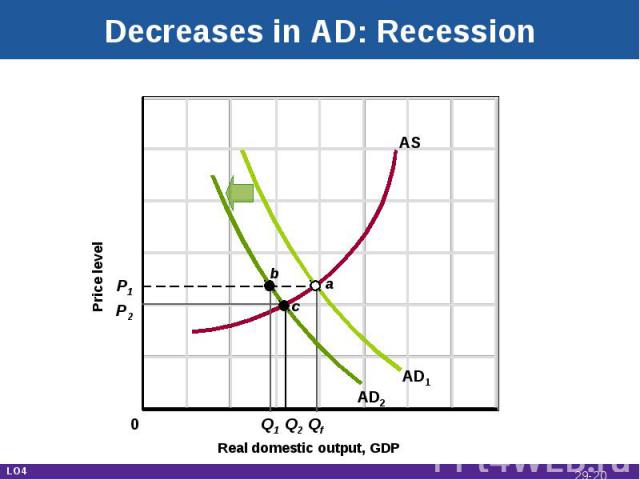
Decreases in AD: Recession Real domestic output, GDP Price level AD1 AS P1 P2 Q1 Q2 Qf AD2 c a b 0 LO4 29-*
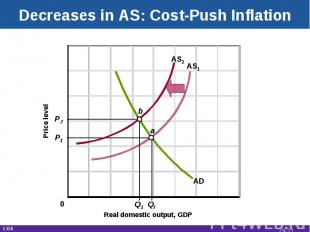
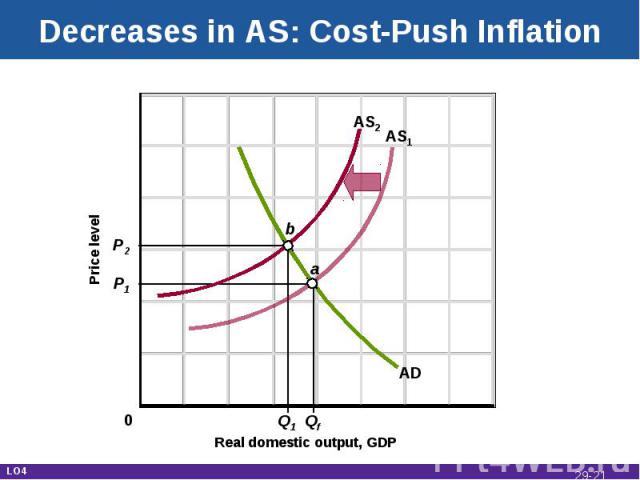
Decreases in AS: Cost-Push Inflation Real domestic output, GDP Price level AD AS1 P1 P2 Q1 Qf AS2 a b 0 LO4 29-*
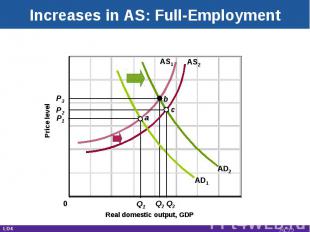
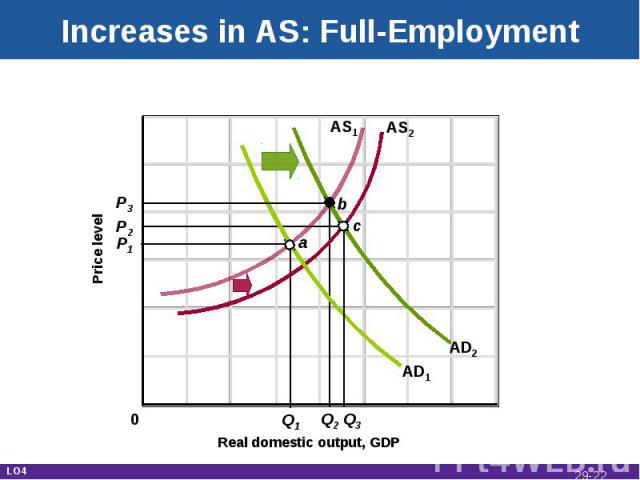
Increases in AS: Full-Employment Real domestic output, GDP Price level AD1 AS2 P1 P2 Q2 Q1 AS1 b AD2 c P3 Q3 a 0 LO4 29-*