Презентация на тему: немецкая классическая философия

ESSAY Theme: Pulmonary Tuberculosis
INTRODUCTION Pulmonary Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that mainly affect the lungs parenchyma. TB is a contagious bacterial (M. tuberculosis)infection that mainly affects the lungs parenchyma, but may spread to other organs.

Incidence and Prevalence 1/3rd of the world’s population is infected with M. tuberculosis Tuberculosis remains one of the top three killers
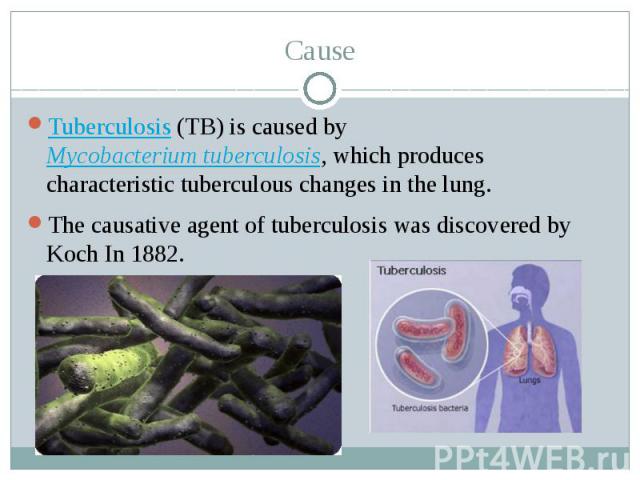
Cause Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which produces characteristic tuberculous changes in the lung. The causative agent of tuberculosis was discovered by Koch In 1882.
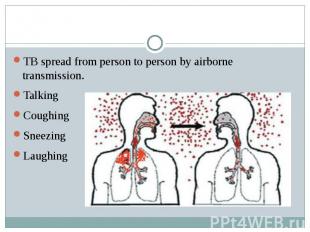
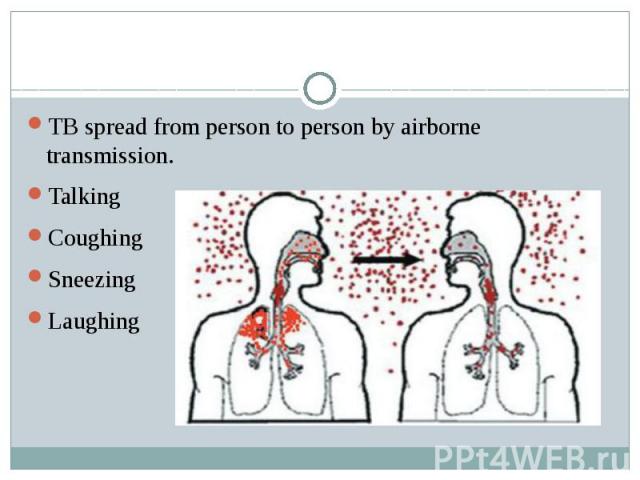
TB spread from person to person by airborne transmission. Talking Coughing Sneezing Laughing

Risk factors CLOSE CONTACT WITH SOME ONE WHO HAVE ACTIVE TB. IMMUNO COMPROMISED STATUS (ELDERLY,CANCER) DRUG ABUSE AND ALCOHOLISM PEOPLE LACKING ADEQUATE HEALTH CARE PRE EXISTING MEDICAL CONDITIONS (DIABETES MELLITUS,CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE) IMMIGRANTS FROM COUNTRIES WITH HIGHER INCIDENCE OF TB. LIVING IN SUBSTANDARD CONDITIONS

Tuberculosis is either latent or active. If you have latent tuberculosis (TB), you do not have symptoms and cannot spread the disease to others. If you have active TB, you do have symptoms and can spread the disease to others.
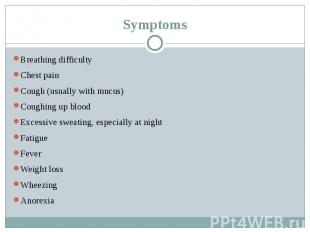
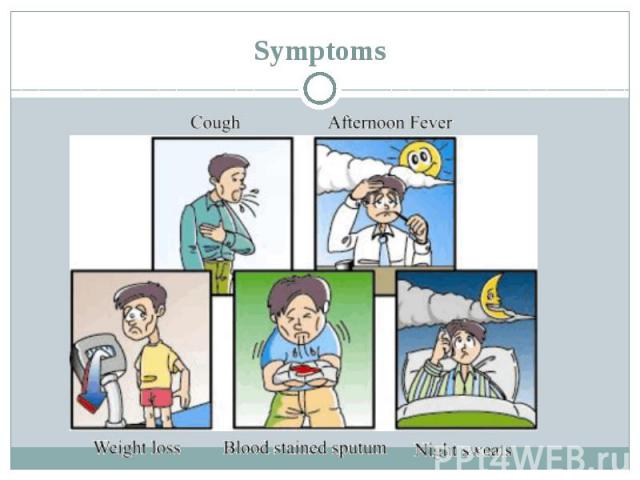
Symptoms Breathing difficulty Chest pain Cough (usually with mucus) Coughing up blood Excessive sweating, especially at night Fatigue Fever Weight loss Wheezing Anorexia
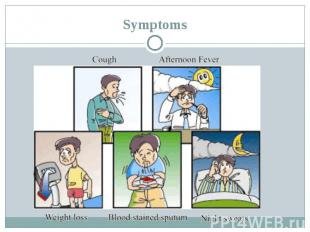
Symptoms
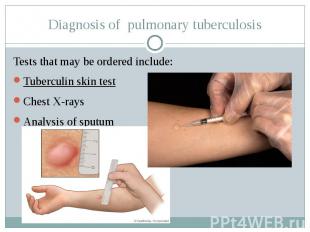
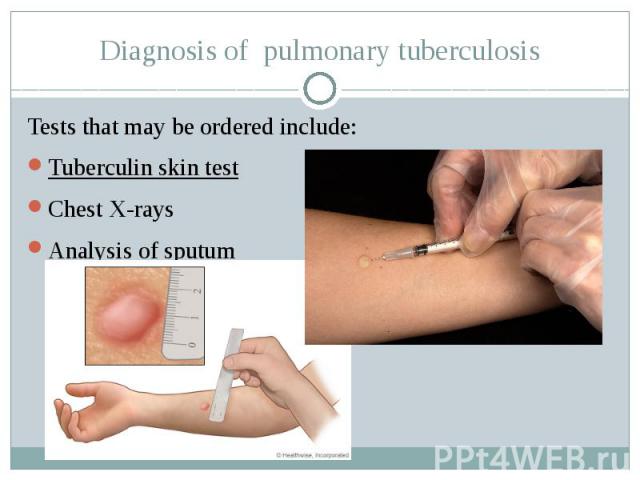
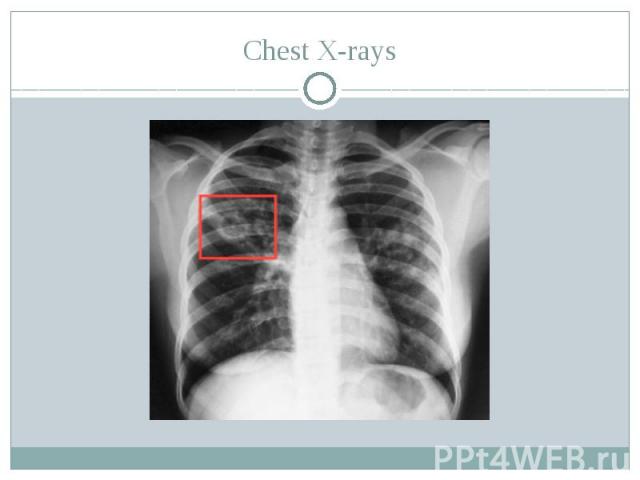
Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis Tests that may be ordered include: Tuberculin skin test Chest X-rays Analysis of sputum
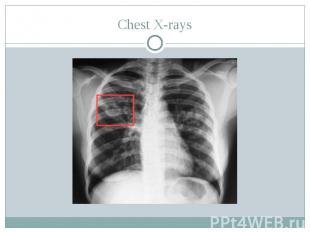
Chest X-rays

Tuberculosis treatment The standard «short» course treatment for tuberculosis (TB), is isoniazid , rifampicin , pyrazinamide , and ethambutol.

Prevention TB is preventable, even in those who have been exposed to an infected person. Skin testing for TB is used in high risk populations or in people who may have been exposed to TB, such as health care workers. Some countries with a high incidence of TB give people a BCG vaccination to prevent TB.

References http://www.medicinenet.com/tuberculosis http://www.stoptb.org http://www.who.int/tb http://www.microbiologybytes.com/video/Mtuberculosis.html http://www.cdc.gov/TB/topic/basics/default.htm