Презентация на тему: History of biotechnology

Applied molecular biology Book: Glick, Pasternak, Molecular Biotechnology, Principles and application of recombinant DNA Biotechnology Molecular genetics

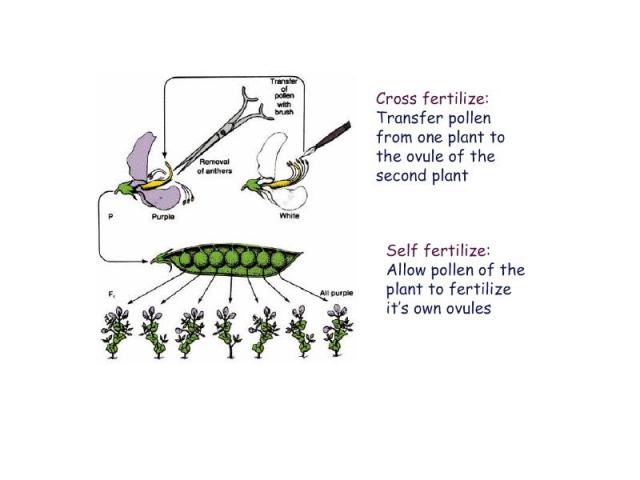
What Is Biotechnology? Using scientific methods with organisms to produce new products or new forms of organisms Any technique that uses living organisms or substances from those organisms to make or modify a product, to improve plants or animals, or to develop microorganisms for specific uses















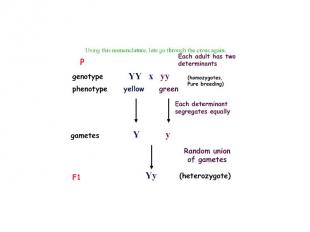
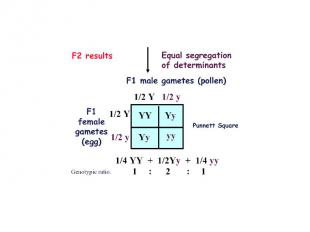
Genetics - historical perspective Practical genetics 7,000 yeas ago corn breeding - Central America rice breeding - China horse pedigree - Babylon













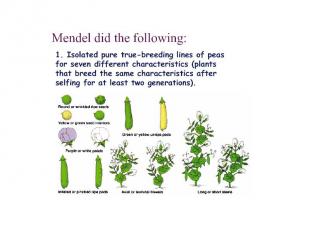

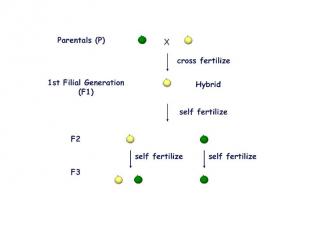
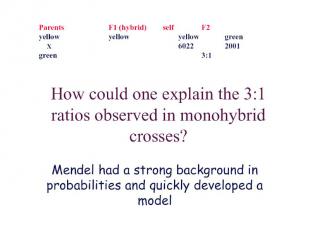
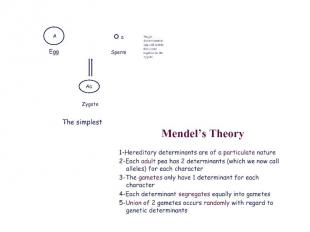

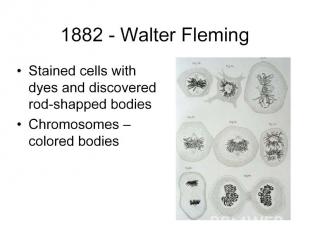

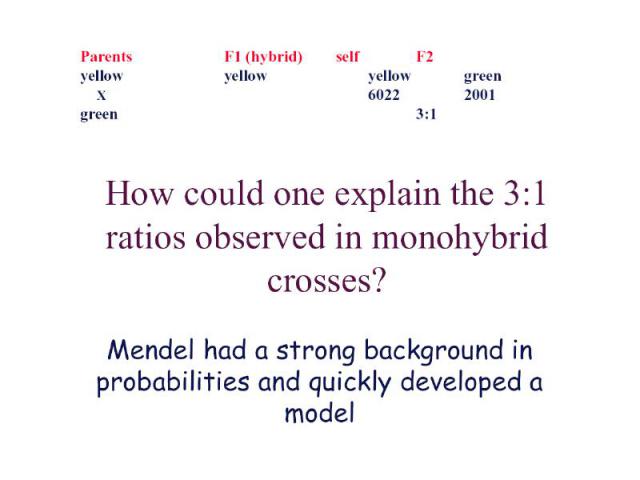
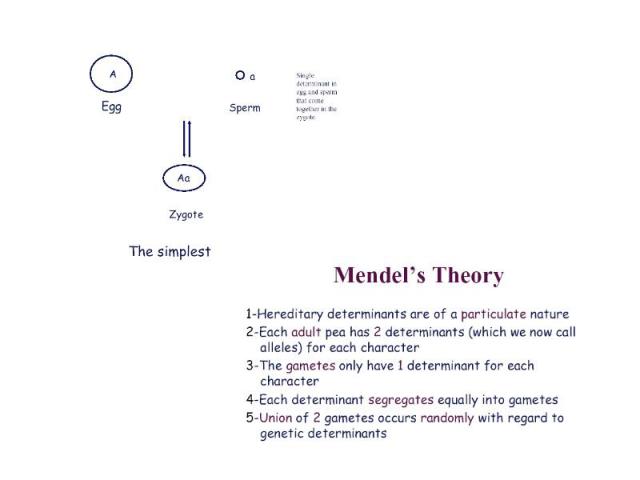
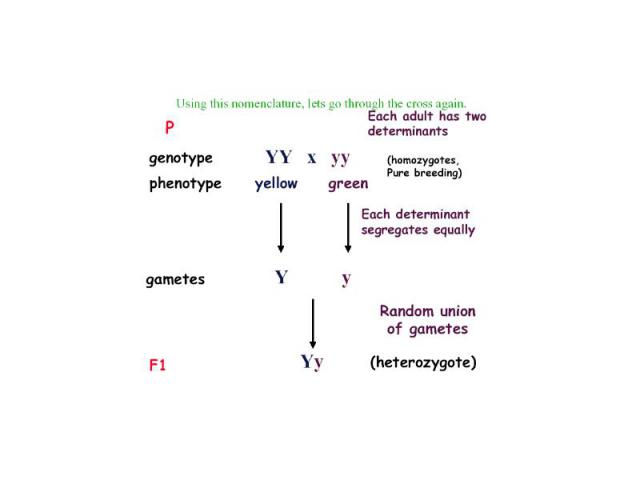
Later Concepts 1900 - Not until 34 years after its publication did Mendel’s work receive additional attention, with publications in 1900 by three Botanists: Hugo de Vries, Carl Correns, and Erich von Tsernak; 1902 - Walter Sutton first integrated the concepts of chromosomes with Mendel’s laws, in studies of grasshopper reproduction and cell division and concluded that Mendel’s heritable factors must be on the chromosomes. 1907 – T.H. Morgan began his work with fruit flies, ultimately mapping gene locations.
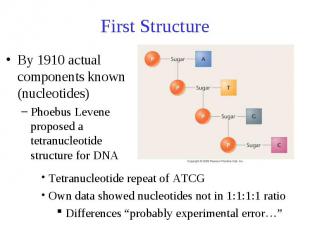
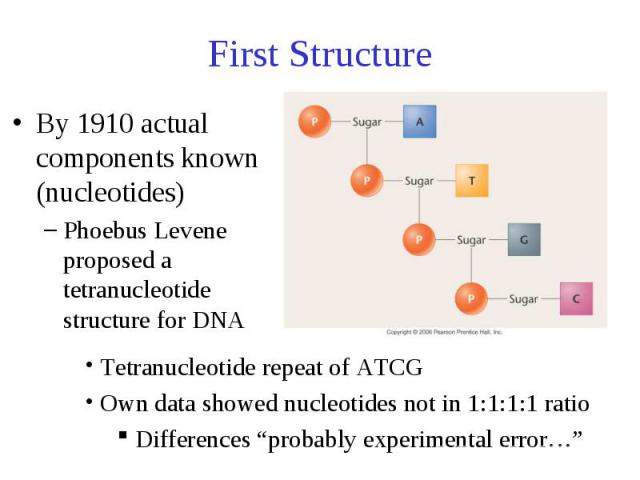
First Structure By 1910 actual components known (nucleotides) Phoebus Levene proposed a tetranucleotide structure for DNA

So… If DNA was a single covalently bonded tetranucleotide structure then it couldn’t easily encode information Proteins, on the other hand, had 20 different amino acids and could have lots of variation Most geneticists focused on “transmission genetics” and passively accepted proteins as being the likely genetic material

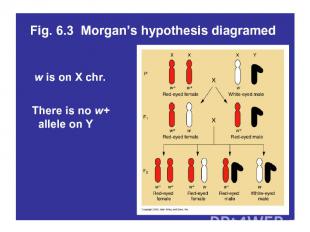
T. H. Morgan’s Fruit Flies 1907-1930s
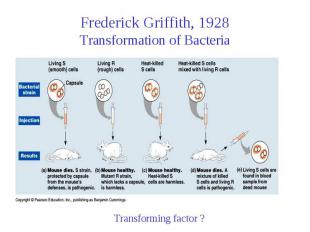
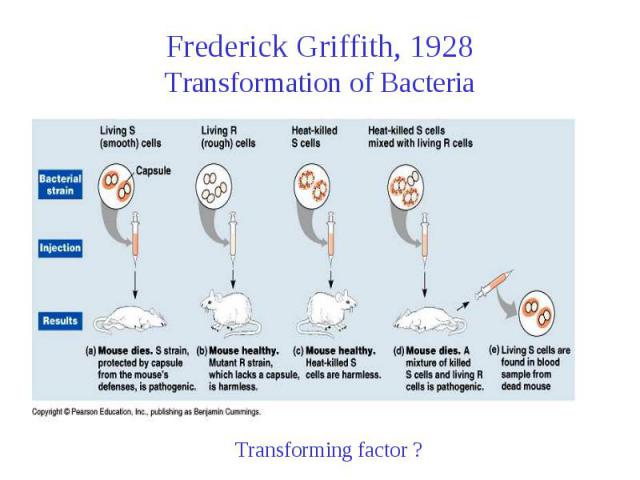
Frederick Griffith, 1928 Transformation of Bacteria

Avery, McCarty and MacLeod After 10 yrs of effort published work using Griffith’s approach to assay for the genetic material Used Cell-free extract of S cells From 75 liters of cell culture obtained 10-25 mg of “active factor Proteases, RNases, DNases, etc. Transforming factor is DNA
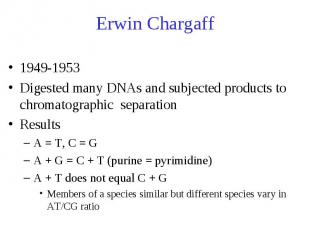
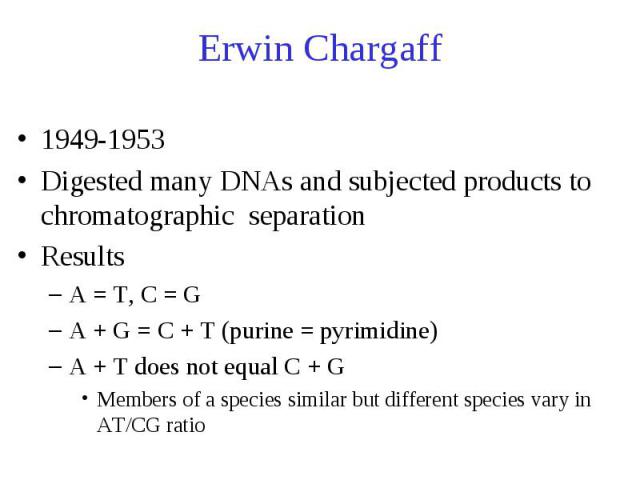
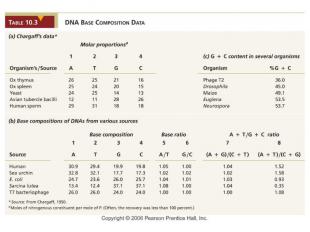
Erwin Chargaff 1949-1953 Digested many DNAs and subjected products to chromatographic separation Results A = T, C = G A + G = C + T (purine = pyrimidine) A + T does not equal C + G Members of a species similar but different species vary in AT/CG ratio
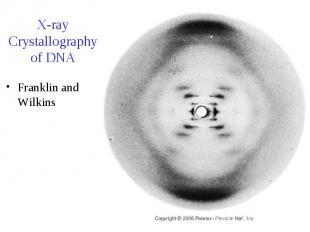
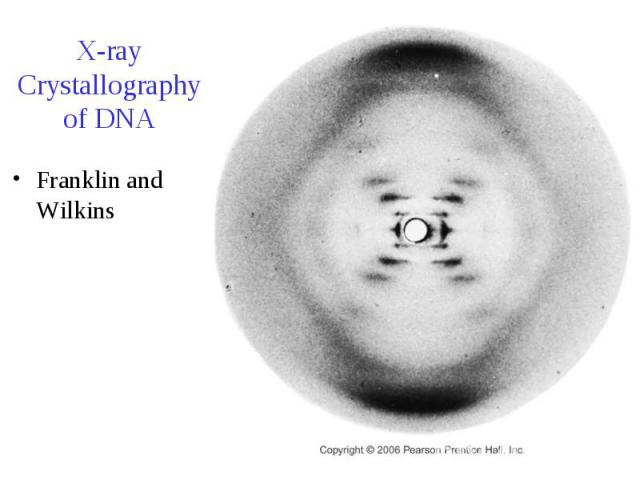
X-ray Crystallography of DNA Franklin and Wilkins

Watson and Crick 1953 propose double helix model Right-handed double helix

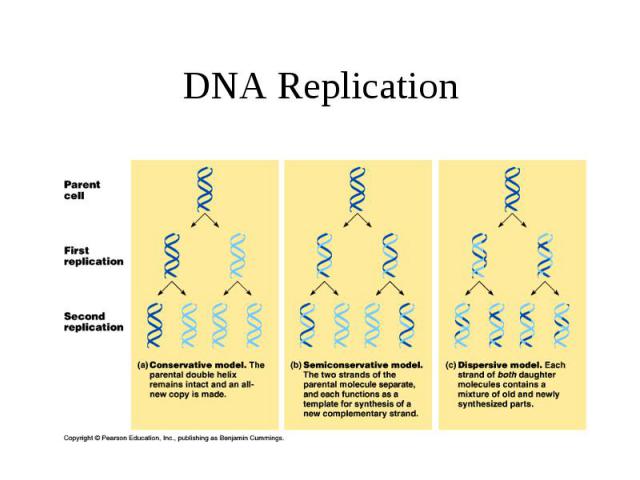
Impact Article in Nature “It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copy mechanism for the genetic material” Second paper 2 months later describes semiconservative replication and that mutations must change bases in DNA (information encoded in the bases and their order) DNA became the genetic material…

DNA Replication