Презентация на тему: Education in Britain

Education in BritainThis project was developed by Nurana Ibragimova and Anna Vasilyeva.

In nursery schools the children learn such things as colours, numbers, letters, and may begin to read and write.

Infant schools Primary education takes place in infant schools (pupils aged from 4/5 to 7 years.

Junior schools
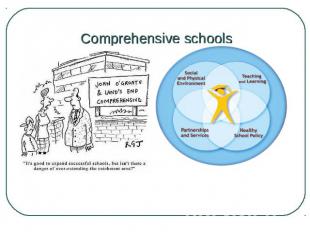
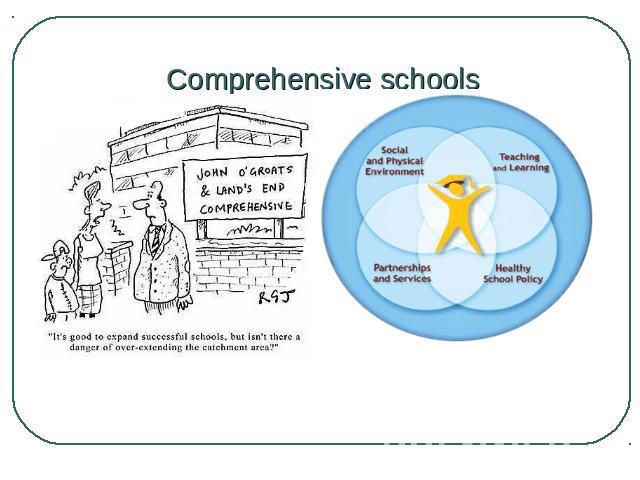
Comprehensive schools Nowadays most British children (over 80 per cent) go to comprehensive schools which take pupils of all abilities without any exams. Comprehensive schools offer a wide choice of subjects from art and craft to the sciences and computer studies.

«Eleven-plus» Before comprehensive schools were introduced in 1965 by the British government all children took an exam at the age of 11 called “eleven-plus”.

Grammar school Those who got the best results at this exam (about 20 per cent) were chosen to go to the best state schools called “grammar schools” which gave secondary education of a rather high standard.

Modern schools Those who failed the 11+ (about 80 per cent) went to secondary modern schools. Secondary modern schools gave secondary education only in name and did not prepare schoolchildren for universities.

GCSE At the end of the fifth form pupils take their first public exam for the General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE).

Private schools Since 1944 free secondary education has been available to all children in Britain. Nevertheless some parents choose to pay for private education.

Independent schools Private or independent schools are called by different names: preparatory (prep) schools are for pupils aged up to 13, and public schools are for 13-to 19-years-olds.

University of Oxford Durham University University of Cambridge University of Bristol Imperial College London University of York
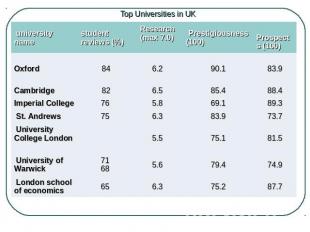
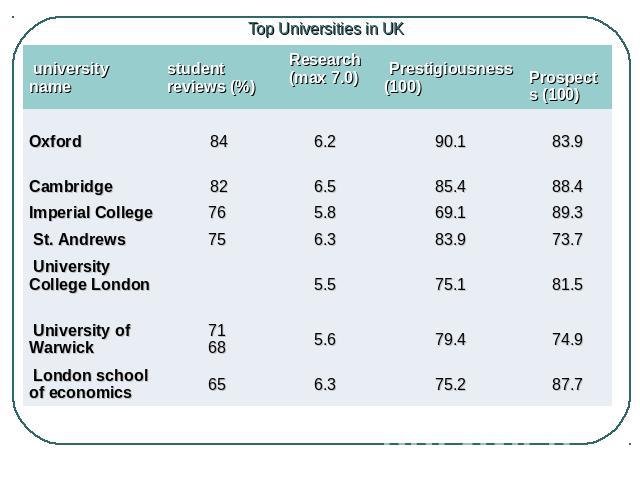
Top Universities in UK

History of the first University of Oxford

Colleges of Oxford College Church of Christ Magdalene College Carfax Tower

Admission to the College The necessary examinations at admission: certifications (IELTS - max 6.5,, TOEFL – max 230); interview with the Commission; grades in school; reference from teachers; good results at A Level.

Libraries In library student can look for information using computer or books, make photocopying, printer documents or just relax.

Graduations Queens College, here are presented in a festive atmosphere diplomas to graduates of Oxford.

Students comments "Most of all, I liked the collegiate structure, which appealed to me as it is less of an imposing 'body' to get involved with. This allows you to play sport and do other things similarly at any level that you like. I play football and cricket for my college and also play recreational rugby and tennis where I can fit it in. "I chose to study at Oxford firstly because I wanted to study at the highest level and stretch my mind; I felt that the Oxford tutorial system was the best environment to achieve this. Secondly because the collegiate system seemed to offer a friendlier atmosphere than a large campus..."

General conclusion. Nurana: ‘During our work on the project I knew a lot of information about education in Great Britain which is very different from the education in Russia. I like the education system in the British schools. I think Russia could enter the same exam as in the United Kingdom which called «eleven-plus». For me this exam shows pupils’ knowledge at the beginning of their education and prepares them to give the very serious exams on the future.’ Anna: ‘Education is the most important thing in the world because it let us get more information about our live, world and ,of course, about future profession. In my project, I studied the system of higher education in Oxford. There are advantages and disadvantages, especially for foreigners. Working on my project, I came to the conclusion that Oxford is designed for talented students. Because in Oxford taught advanced course in each subject.’