Презентация на тему: Ecological problems in Ukraine and Great Britain

Ecological problems

Ecological problems in Ukraine 4. Destruction of soil
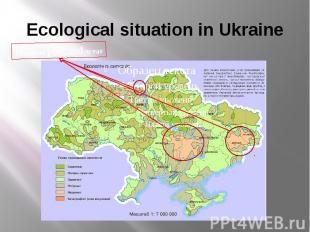
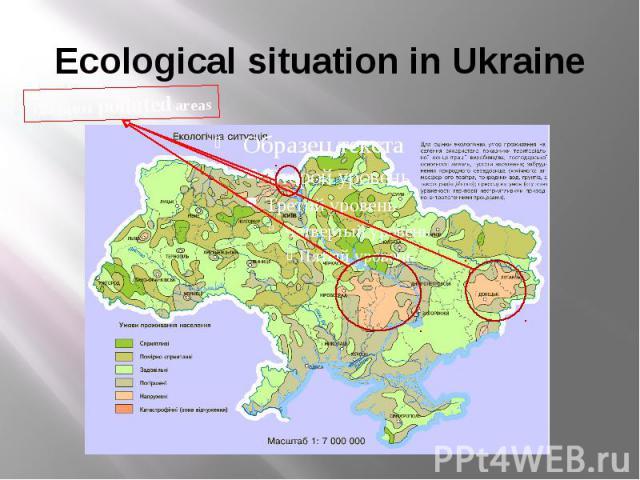
Ecological situation in Ukraine
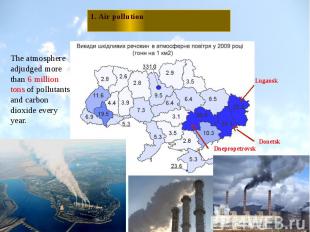
1. Air pollution

2. Acid rain

3. Water pollution

4.Destruction of soil

5. Recycling of wastes The total area of all polygons with waste is already more than 150 hectares (4% of the country). Substances that are released as a result of chemical reactions are able to turn the territory of Ukraine in a continuous zone of ecological disaster.

6. Deforestation

7. Chernobyl disaster

Environmental protection in Ukraine Ukraine is cooperating with international ecological organization such as “Greenpeace”. Environmental safeguards of conservation water resources have become more stringent. Ways to overcome the ecological crisis in Ukraine: Develop programme of cardinal recovery of environment and create clean conditions for the present and future generations Develop and approve the Environmental Policy of Ukraine to address every region Provide ecological monitoring system at all levels Use the best foreign practices to create an effective system of environmental safety Provide prohibition of deforestation

Ecological problems in United Kingdom 2. Water pollution

1. Air pollution Smog is a type of air pollutant. This kind of smog is caused by the burning of large amounts of coal within a city; this smog contains soot particulates from smoke, sulfur dioxide and other components.

2. Water pollution Nuclear waste from nuclear plants is discharged into the Irish Sea, making it one of the most radioactive seas in the world.

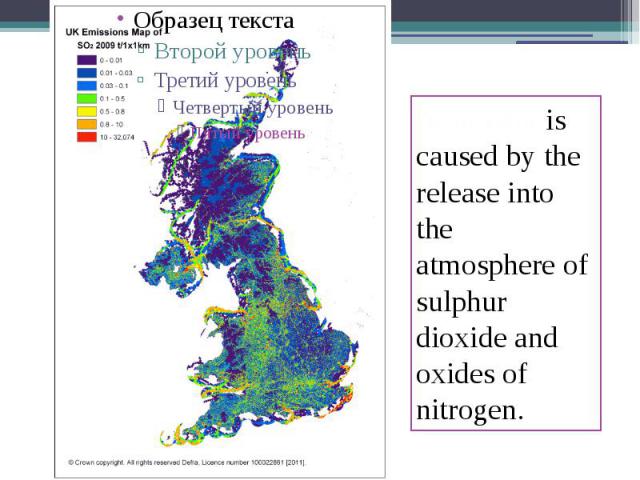
3. Acid rain Acid rain also damages trees buildings, statues and can kill fish in lakes and rivers. They are caused by smoke from factories and power stations and exhaust fumes from transport. It is produced when coal and oil are burnt.
Acid rain is caused by the release into the atmosphere of sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen.

4. Climate change

5. Deforestation

6. Waste A significant proportion of food waste is produced by the domestic household, which, in 2007, created 6,700,000 tonnes of food waste.

7. Soil pollution Contaminated or polluted soil directly affects human health through direct contact with soil. Mercury and cyclodienes – kidney damage Benzene – higher incidence of leukemia Organophosphates and carbonates – neuromuscular blockage

Environmental protection in UK Great Britain careful checks on use of dangerous chemicals Great Britain has adopted a phased programme of reductions in sulphur dioxide emissions from existing large combustion plants of up to 60 per cent by 2003. Ten National parks have been established in England and Wales, four — in Scotland. Water pollution programmes are being worked out in Great Britain nowadays Responsibility for pollution control is divided between local authorities and central government. To prevent air pollution we need to look for other ways of supplying energy. Recycling saves energy and raw materials.