Презентация на тему: Biotransformation

BIOTRANSFORMATION DR. NASIR ALI AFSAR

CLEARANCE OF DRUGS Definition Why needed? Either Unchanged Metabolites Polarity of compounds
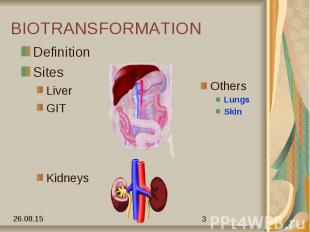
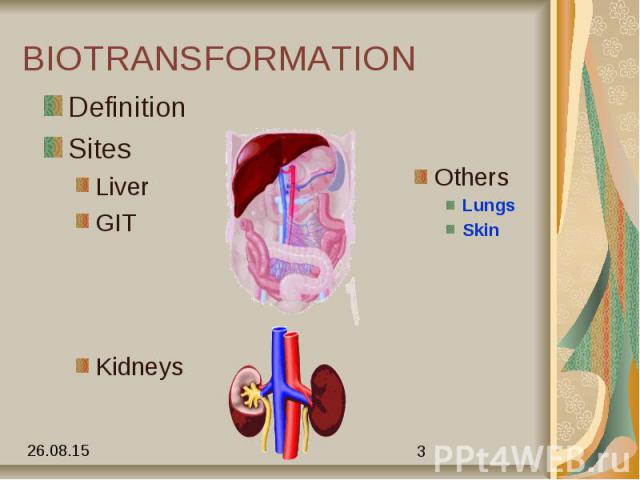
BIOTRANSFORMATION Definition Sites Liver GIT Kidneys

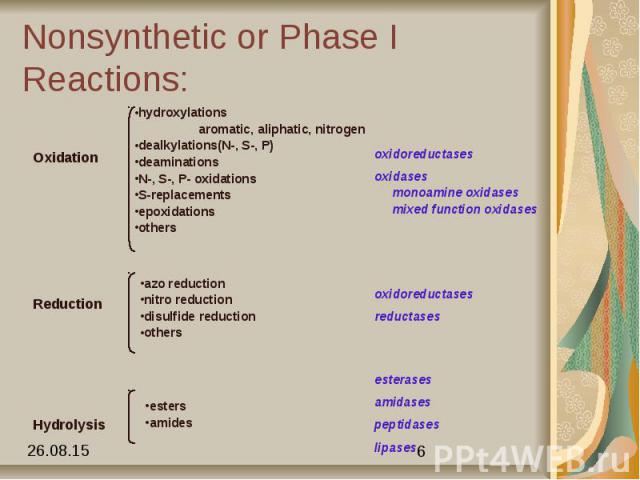
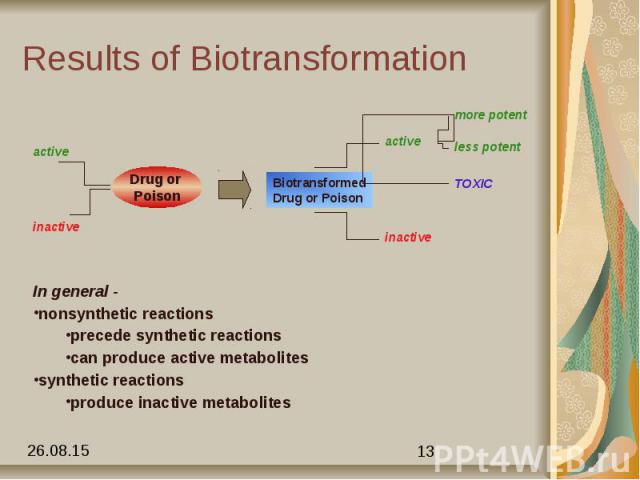
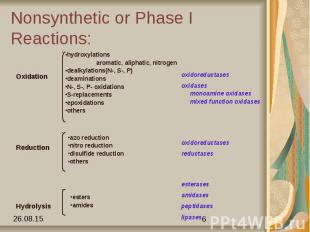
Phases Phase I - Nonsynthetic make polar by unmasking a functional group like -OH, -NH2, -SH. oxidation-add O, remove H reduction-remove O, add H hydrolysis - add H2O Phase II - Synthetic make very polar Generally act in tandem
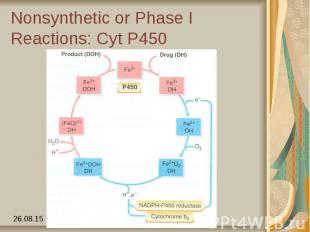
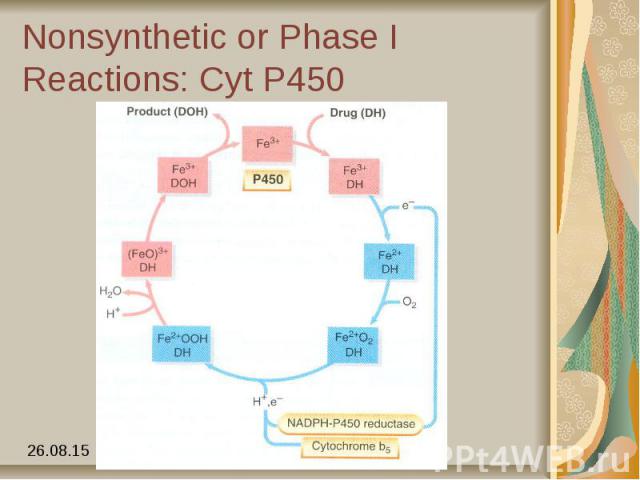
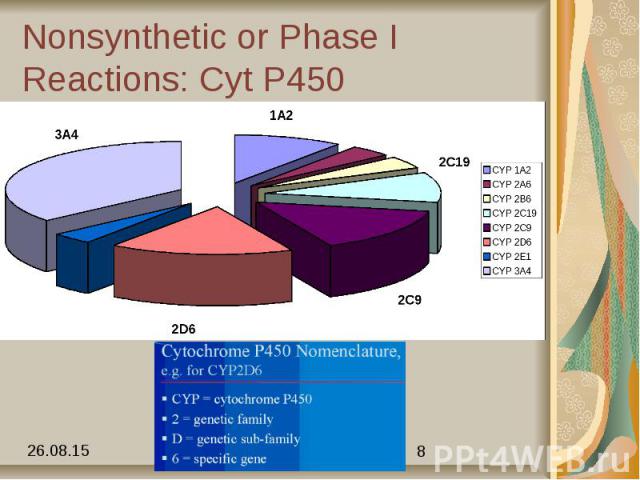
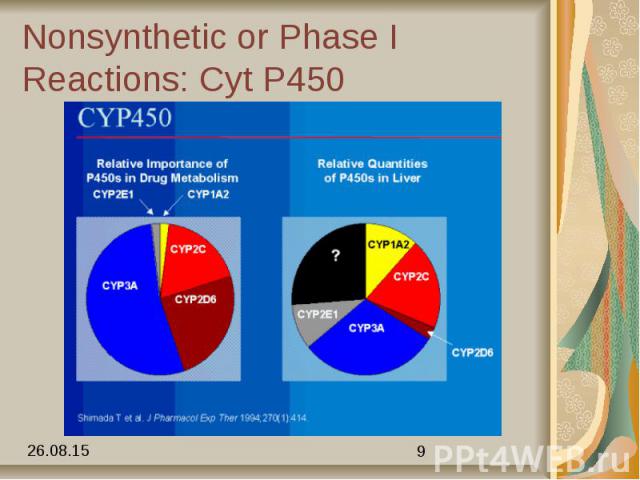
Nonsynthetic or Phase I Reactions: Cyt P450



Enzyme Induction Enhance synthesis: Phenobarbital, Steroids Reduce rate of degradation: ‘Substrate Stabilization’ Clotrimazole, Ethanol

Enzyme Inhibition Binding/Inactivation of heme iron: Imidazoles, Macrolides Inactivation of the enzyme protein: suicide inhibitors: Chloramphenicol combination of above: Secobarbital

Synthetic or Phase II Reactions: Involves high energy intermediates Glucuronidation, Acetylation, Methylation, Glutathione/ Glycine/ Sulfate/ Water Conjugation. Transferases in microsomes or cytosol Role of nutrition in regulation of drug conjugation
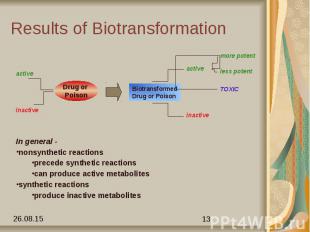

Clinical Relevance Individual Differences Age & Sex Genetic Factors Diet & Environmental factors Drug interactions Diseases