Презентация на тему: Volcanoes: Eruptions and Hazards

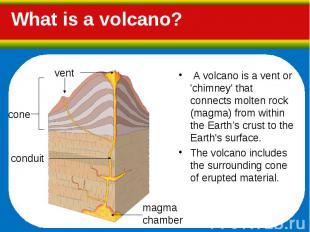
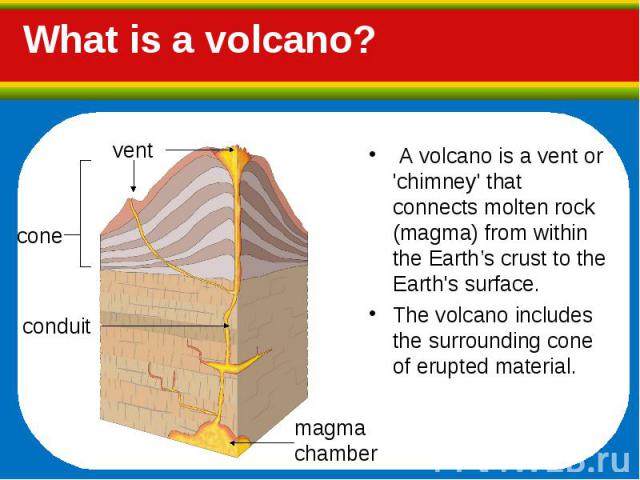
A volcano is a vent or 'chimney' that connects molten rock (magma) from within the Earth’s crust to the Earth's surface. A volcano is a vent or 'chimney' that connects molten rock (magma) from within the Earth’s crust to the Earth's surface. The volcano includes the surrounding cone of erupted material.



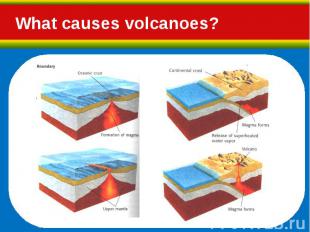
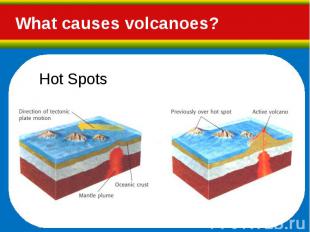

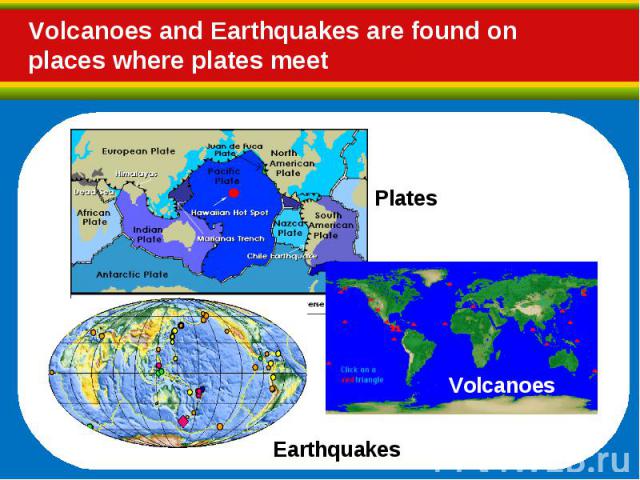
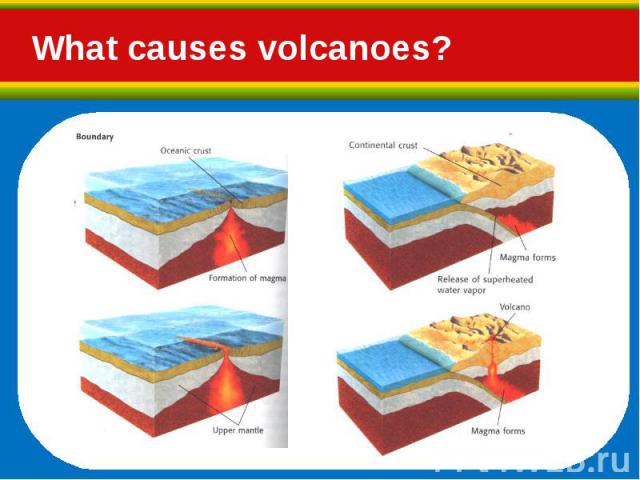
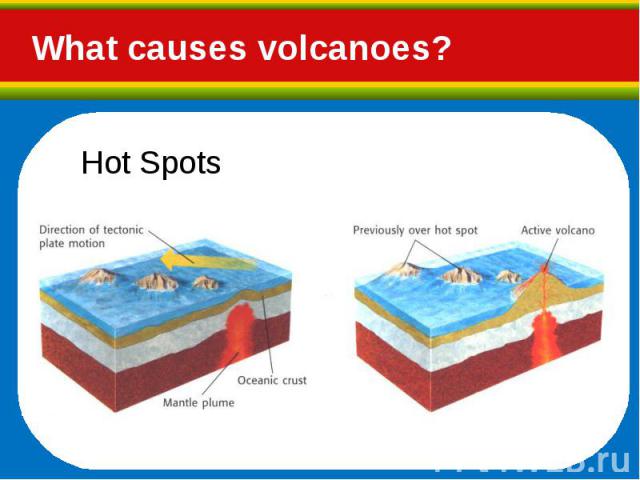
Hot, molten rock (magma) is buoyant (has a lower density than the surrounding rocks) and will rise up through the crust to erupt on the surface. Hot, molten rock (magma) is buoyant (has a lower density than the surrounding rocks) and will rise up through the crust to erupt on the surface. Same principle as hot air rising, e.g. how a hot air balloon works When magma reaches the surface it depends on how easily it flows (viscosity) and the amount of gas (H2O, CO2, S) it has in it as to how it erupts.


High content High content More likely to be !!! High content More likely to be !!! Why? Silica has a thick, stiff consistency Flows slowly Tends to Harden in the volcano’s vent






Explosive volcanic eruptions can be catastrophic Explosive volcanic eruptions can be catastrophic Erupt 10’s-1000’s km3 of magma Send ash clouds >25 km into the stratosphere Have severe environmental and climatic effects Hazardous!!!

Three products from an explosive eruption Three products from an explosive eruption Ash fall Pyroclastic flow Pyroclastic surge

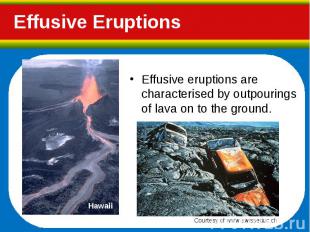
Effusive eruptions are characterised by outpourings of lava on to the ground. Effusive eruptions are characterised by outpourings of lava on to the ground.

Pyroclastic flow Pyroclastic flow Lahars/Mud flows Pyroclastic fall Lava flow Noxious Gas Earthquakes

For example, eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD destroyed the city of Pompeii For example, eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD destroyed the city of Pompeii

On August 24, 79AD Mount Vesuvius literally blew its top, erupting tonnes of molten ash, pumice and sulfuric gas miles into the atmosphere. Pyroclastic flows flowed over the city of Pompeii and surrounding areas. On August 24, 79AD Mount Vesuvius literally blew its top, erupting tonnes of molten ash, pumice and sulfuric gas miles into the atmosphere. Pyroclastic flows flowed over the city of Pompeii and surrounding areas.

Pyroclastic flows of poisonous gas and hot volcanic debris engulfed the cities of Pompeii, Herculaneum and Stabiae suffocating the inhabitants and burying the buildings. Pyroclastic flows of poisonous gas and hot volcanic debris engulfed the cities of Pompeii, Herculaneum and Stabiae suffocating the inhabitants and burying the buildings.

The cities remained buried and undiscovered for almost 1700 years until excavation began in 1748. These excavations continue today and provide insight into life during the Roman Empire. The cities remained buried and undiscovered for almost 1700 years until excavation began in 1748. These excavations continue today and provide insight into life during the Roman Empire.


Hot volcanic activity can melt snow and ice Hot volcanic activity can melt snow and ice Melt water picks up rock and debris Forms fast flowing, high energy torrents Destroys all in its path


It is not just explosive volcanic activity that can be hazardous. Effusive (lava) activity is also dangerous. It is not just explosive volcanic activity that can be hazardous. Effusive (lava) activity is also dangerous.

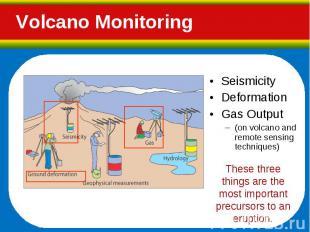
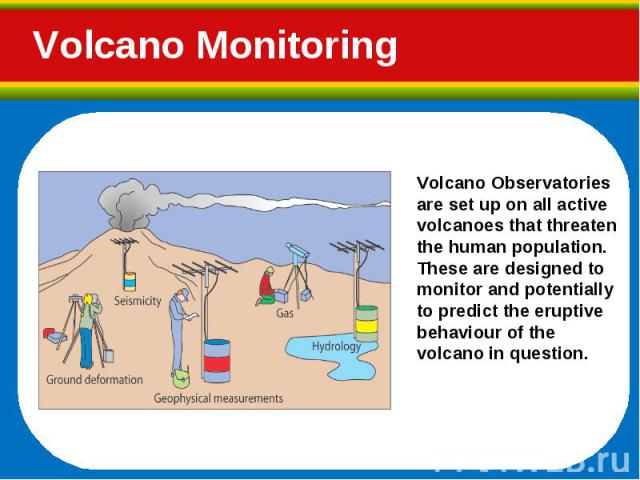
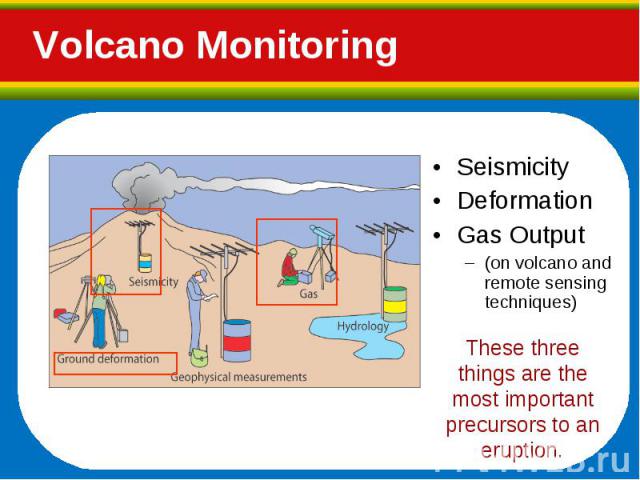
Seismicity Seismicity Deformation Gas Output (on volcano and remote sensing techniques)

Gas samples are collected from fumaroles and active vents. Gas samples are collected from fumaroles and active vents. Gas levels may also be monitored by remote sensing techniques

Volcanoes are extremely hazardous. Volcanoes are extremely hazardous. However, the volcano can be studied, monitored and understood. Each volcano is different, and offers a unique set of dangers Plans may be emplaced to help control potential damage.