Презентация на тему: THE ENVIRONMENT



Environment – oкружающая среда Environment – oкружающая среда To protect – охранять Recycling – вторичная переработка To pollute – загрязнять Pollution - загрязнение Bad breath - выхлопные газы Chemicals – химические отходы Acid rains – кислотные дожди Wastes – отходы Trash, litter – хлам, мусор To harm – причинять вред Pesticides – хим. средства для борьбы с вредителями Energy “leaks” –утечка энергии

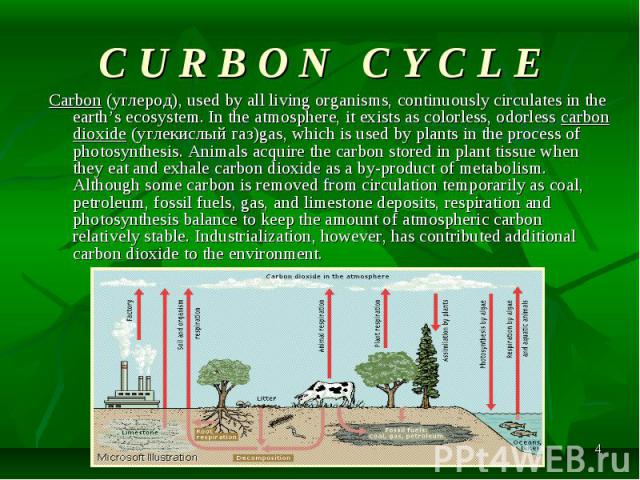
Carbon (углерод), used by all living organisms, continuously circulates in the earth’s ecosystem. In the atmosphere, it exists as colorless, odorless carbon dioxide (углекислый газ)gas, which is used by plants in the process of photosynthesis. Animals acquire the carbon stored in plant tissue when they eat and exhale carbon dioxide as a by-product of metabolism. Although some carbon is removed from circulation temporarily as coal, petroleum, fossil fuels, gas, and limestone deposits, respiration and photosynthesis balance to keep the amount of atmospheric carbon relatively stable. Industrialization, however, has contributed additional carbon dioxide to the environment. Carbon (углерод), used by all living organisms, continuously circulates in the earth’s ecosystem. In the atmosphere, it exists as colorless, odorless carbon dioxide (углекислый газ)gas, which is used by plants in the process of photosynthesis. Animals acquire the carbon stored in plant tissue when they eat and exhale carbon dioxide as a by-product of metabolism. Although some carbon is removed from circulation temporarily as coal, petroleum, fossil fuels, gas, and limestone deposits, respiration and photosynthesis balance to keep the amount of atmospheric carbon relatively stable. Industrialization, however, has contributed additional carbon dioxide to the environment.
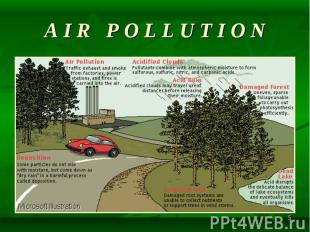

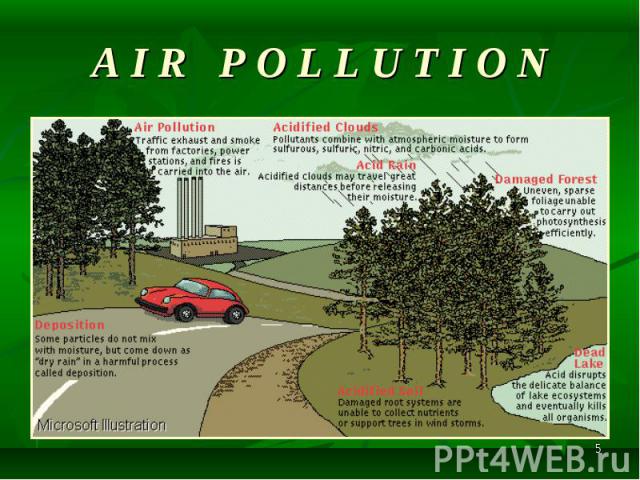
Carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and other types of contaminants pouring from industrial smokestacks contribute to worldwide atmospheric pollution. Carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and other types of contaminants pouring from industrial smokestacks contribute to worldwide atmospheric pollution. Carbon dioxide contributes significantly to global warming, while sulfur dioxide is the principal cause of acid rain. Other environmental problems stemming from smokestack emissions include respiratory diseases, poisoned lakes and streams, and damaged forests and crops.

Automobile exhaust contains a number of airborne pollutants that adversely affect the health of animals and plants and the chemical nature of the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide and hydrocarbon emissions, two of the major components of automobile exhaust, contribute significantly to global warming and are produced as a by-product of the combustion of petroleum-based fuels. Elevated carbon dioxide and hydrocarbon levels cause sunlight to be reflected and trapped within the atmosphere, which slowly raises the temperature of the atmosphere. Automobile exhaust contains a number of airborne pollutants that adversely affect the health of animals and plants and the chemical nature of the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide and hydrocarbon emissions, two of the major components of automobile exhaust, contribute significantly to global warming and are produced as a by-product of the combustion of petroleum-based fuels. Elevated carbon dioxide and hydrocarbon levels cause sunlight to be reflected and trapped within the atmosphere, which slowly raises the temperature of the atmosphere.

Thermal Inversion Thermal Inversion (тепловые аномалии) Smog (туман) surrounds the Angel Monument in Mexico City, Mexico, during a thermal inversion. Air pollution increases dramatically as a mass of cold air is trapped below a warmer mass of air. The absence of wind circulation prevents pollution near the earth’s surface from escaping.


In the 1970s and 1980s, scientists began to find that human activity was having a detrimental effect on the global ozone layer, a region of the atmosphere that shields the earth from the sun's harmful ultraviolet rays. Without this gaseous layer, which is about 40 km (about 25 mi) thick, no life could survive on the planet In the 1970s and 1980s, scientists began to find that human activity was having a detrimental effect on the global ozone layer, a region of the atmosphere that shields the earth from the sun's harmful ultraviolet rays. Without this gaseous layer, which is about 40 km (about 25 mi) thick, no life could survive on the planet

Forest Damaged by Acid Rain Forest Damaged by Acid Rain Forests, lakes, ponds, and other terrestrial and aquatic environments throughout the world are being severely damaged by the effects of acid rain. Acid rain is caused by the combination of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen compounds with water in the atmosphere. In addition to chemically burning the leaves of plants, acid rain poisons lake water, killing most, if not all, the aquatic inhabitants.

Acid rain is a major global problem. Acid rain corrodes metals, weathers stone buildings and monuments, injures and kills vegetation, and acidifies lakes, streams, and soils, especially in the poorly buffered regions of northeastern North America and northern Europe . Acid rain is a major global problem. Acid rain corrodes metals, weathers stone buildings and monuments, injures and kills vegetation, and acidifies lakes, streams, and soils, especially in the poorly buffered regions of northeastern North America and northern Europe . It is estimated that each year 10 million people die worldwide from drinking contaminated water.

Exxon Valdez Oil Spill Cleanup Exxon Valdez Oil Spill Cleanup Workers washed the shoreline on Latouche Island, Alaska after the Exxon Valdez oil tanker ran aground in 1989, dumping more than 380 million liters (10 million gallons) of oil into Prince William Sound. The resulting environmental damage prompted the United States Congress to pass federal safety requirements for oil tankers and barges and to assign the principal cost of spill cleanup to oil companies.




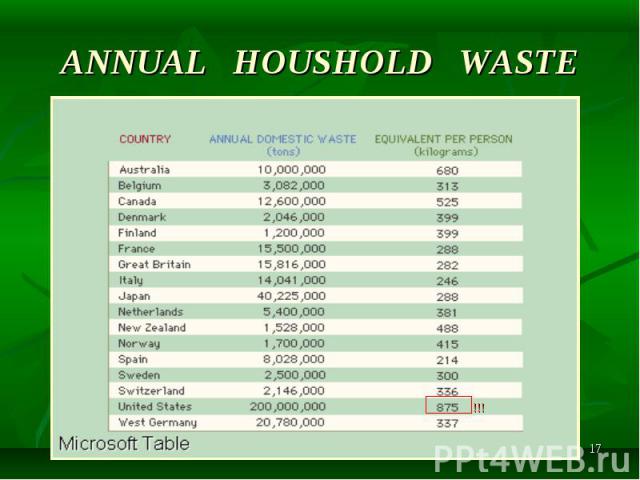
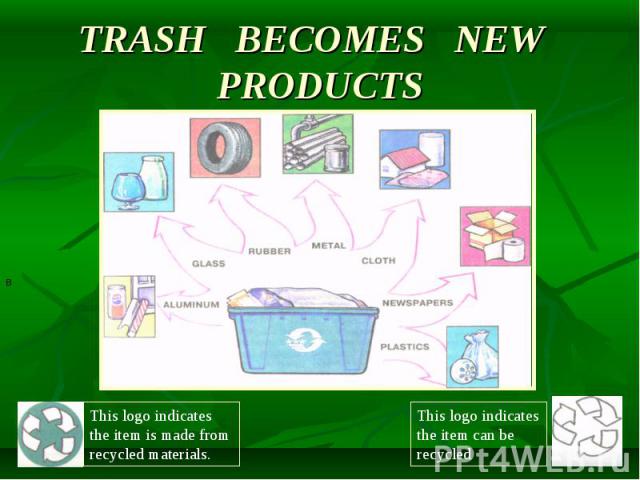
An average city dweller may produce a ton of refuse in a year, a volume that rapidly overflows local dumps. Cities running out of space for landfill often turn to incinerating their waste or transporting it to other areas, although up to 90 percent of the material might have been recycled. An average city dweller may produce a ton of refuse in a year, a volume that rapidly overflows local dumps. Cities running out of space for landfill often turn to incinerating their waste or transporting it to other areas, although up to 90 percent of the material might have been recycled.



Recycling Aluminum Cans Recycling Aluminum Cans In an effort to conserve nonrenewable natural resources, many industries and individuals recycle waste aluminum. At this collection point, the Alcoa Recycling Company in New Jersey processes aluminum cans into large bales.
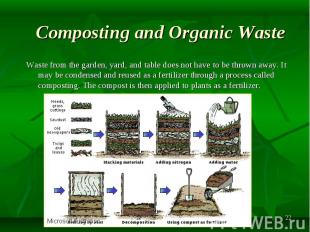
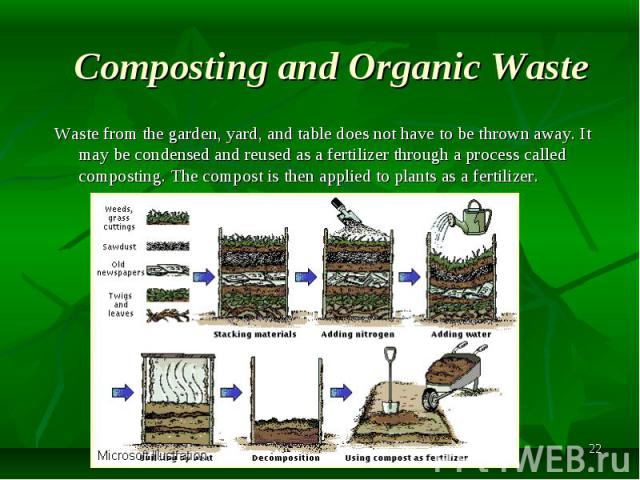
Waste from the garden, yard, and table does not have to be thrown away. It may be condensed and reused as a fertilizer through a process called composting. The compost is then applied to plants as a fertilizer.

Garbage is converted to useful energy in this solid waste plant. Garbage is converted to useful energy in this solid waste plant.

What can cause air pollution? What can cause air pollution? What does acid rain harm? Where do some companies dump their chemical waste? What kinds of energy are renewable? What is an “ energy leak” and what are the ways of solving this problem? Why do farmers spray chemicals on crops? Why do you think recycling programs are important? Is there a lot of trash in your village? What noble work do the people of “Greenpeace” do? Why must technology bring apology to ecology? What do you think you should do to protect the environment? MAKE A POSTER CALLING TO PROTECT THE ENVIRONMENT.