Презентация на тему: Steganography

Steganography By Tukenov Ilyas & Tleuov Adilet

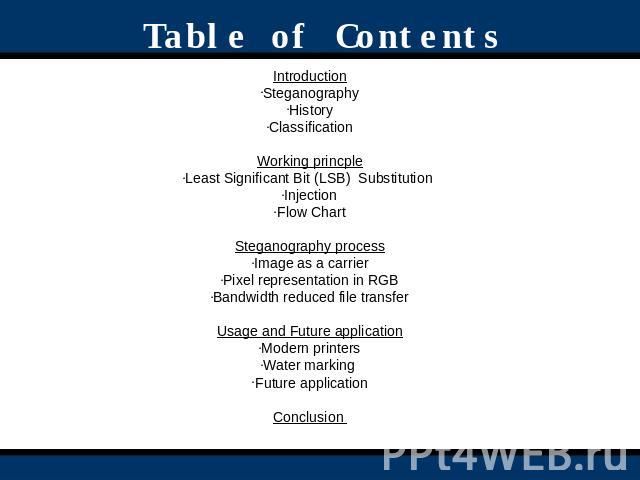
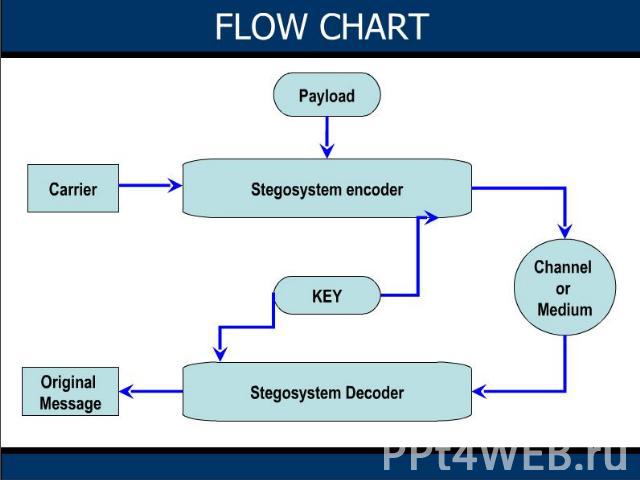
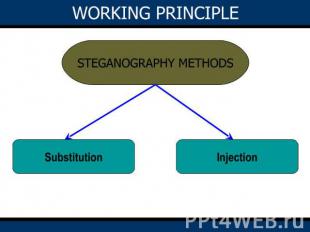
Table of Contents IntroductionSteganographyHistoryClassificationWorking princpleLeast Significant Bit (LSB) Substitution InjectionFlow ChartSteganography processImage as a carrierPixel representation in RGBBandwidth reduced file transferUsage and Future applicationModern printersWater marking Future applicationConclusion
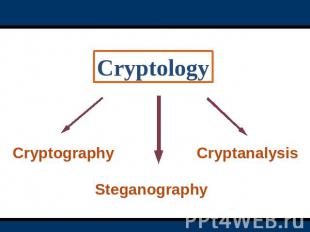
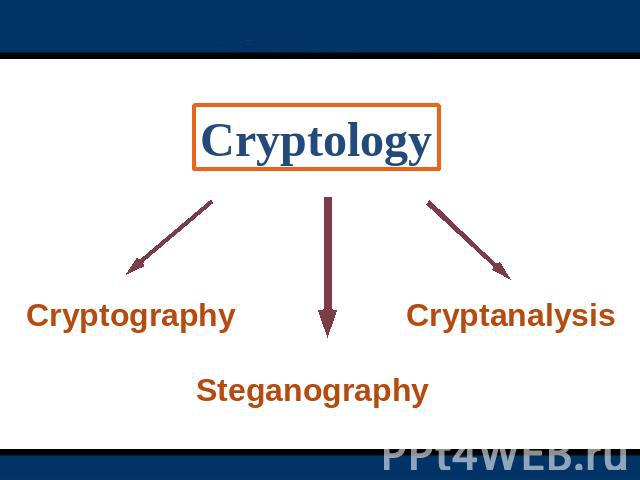
Cryptology CryptographySteganographyCryptanalysis





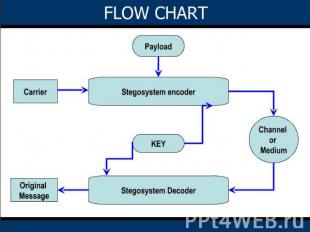

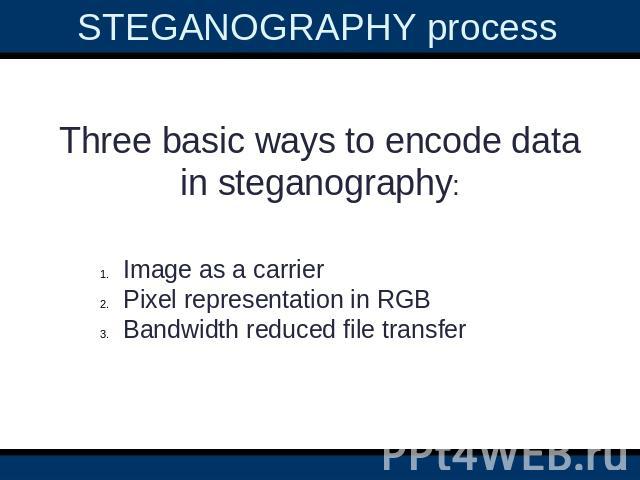
STEGANOGRAPHY process Three basic ways to encode data in steganography:Image as a carrierPixel representation in RGBBandwidth reduced file transfer

1.IMAGE AS CARRIER: It is an efficient technique for steganography, An image is used as cover for hiding the actual data. Digital images are a preferred media for hiding information due to their high capacity and low impact on visibility.2.PIXEL REPRESETATION IN RGB:Basic RGB color model, every pixel is represented by the four bytes namely Alpha, red, green, blue Alpha: degree of transparency Red: intensity of red color Green: intensity of green color Blue: intensity of blue colorThe alpha bit is used to carry the data, as it has no much importance in image representation.

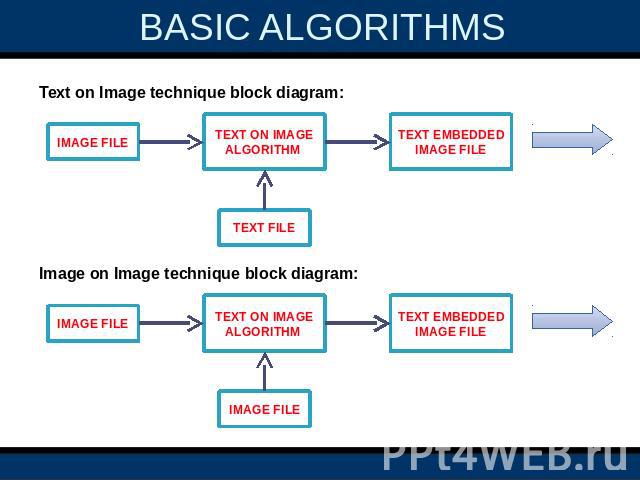
3.BANDWIDTH REDUCED TRANSMISSION: If an image data takes six minutes to transfer between two systems and a text file takes 3 minutes. One can use steganography technique in order to reduce the time taking by embedding the text in the image and the total content will be transferred in six minutes. Two basic algorithms used for steganography areText on Image algorithm.Image on Image algorithm.

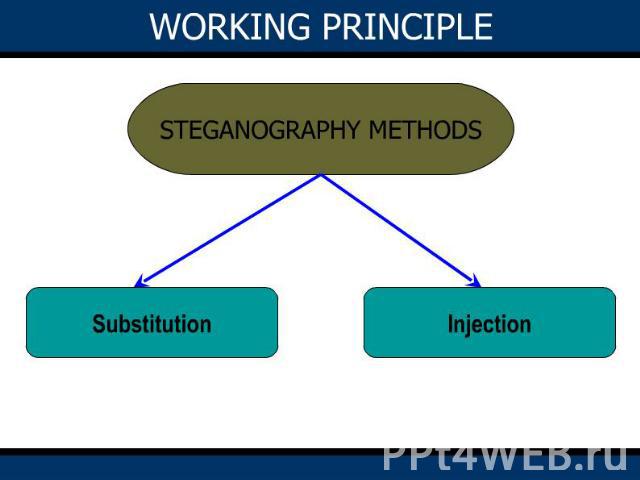
BASIC ALGORITHMS Two basic algorithms used for steganographyText on Image algorithm.Image on Image algorithm.
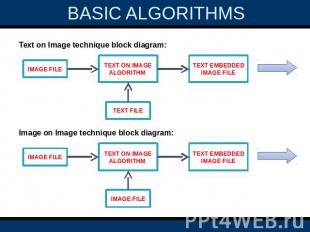
BASIC ALGORITHMS
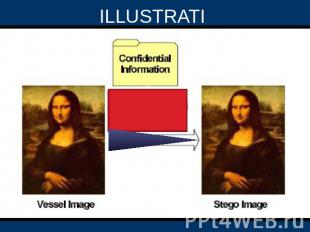
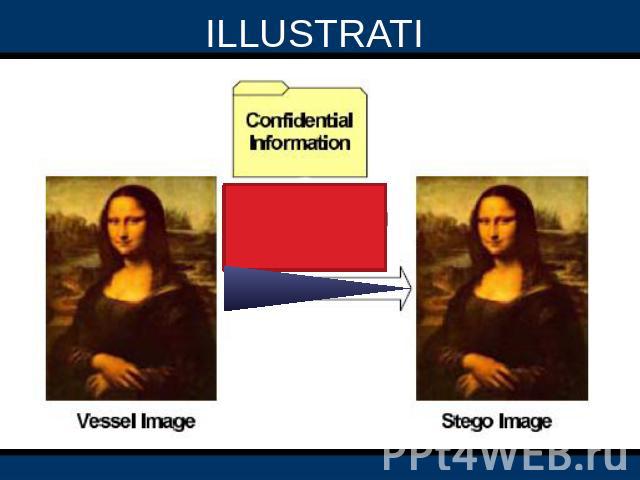
ILLUSTRATION

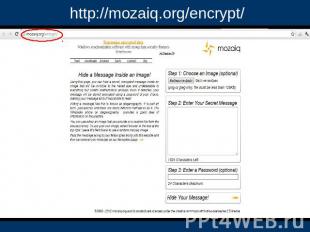
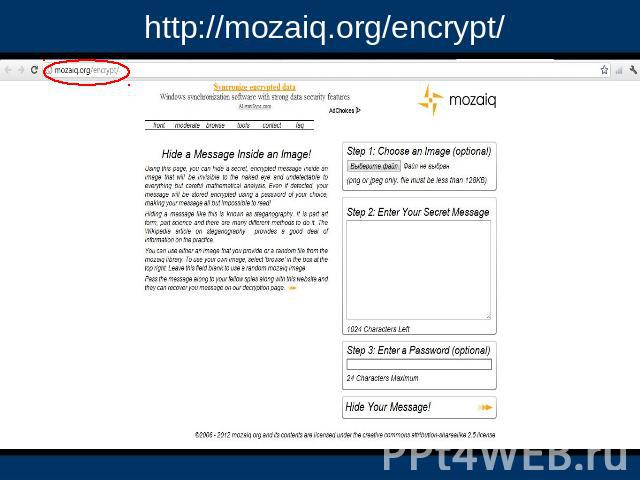
http://mozaiq.org/encrypt/

ADVANTAGES Internet privacy.Secret communication between the organizations like boarder security force and defense organization.Effective than that of cryptography.Additional layer for security than cryptography.



Thank you!