Презентация на тему: Periodisation of English


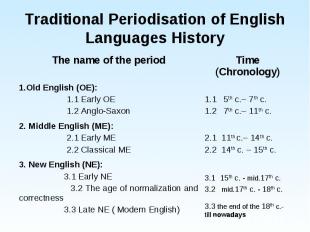
Traditional Periodisation of English Languages History. Traditional Periodisation of English Languages History. Professor Rastorguyeva’s Periodisation. Old English. Middle English: 4.1 Early Middle English 4.2 Classical Middle English. New English: 5.1 Early New English 5.2 the age of Normalization and Correctness 5.3 Modern English.

The commonly accepted, traditional periodisation divides English language history into three periods: The commonly accepted, traditional periodisation divides English language history into three periods: Old English (OE); Middle English (ME); New or Modern English (NE, Mod E).

This periodisation of English language history is partly based on the conventional three periods. This periodisation of English language history is partly based on the conventional three periods. It subdivides the history of the English language into seven periods.


At the begging it was the stage of tribal dialects of the WG invaders, which were gradually losing contacts with the related continental languages. At the begging it was the stage of tribal dialects of the WG invaders, which were gradually losing contacts with the related continental languages. The tribal dialects were only used for oral communication. The 7th century is the beginning of writing, the tribal dialects gradually changed into local or regional dialects.

OE was a typical OG language, with a purely Germanic vocabulary, and few foreign borrowings. As far as grammar is concerned, OE was an inflected or “synthetic” language with a well-developed system of morphological categories. OE was a typical OG language, with a purely Germanic vocabulary, and few foreign borrowings. As far as grammar is concerned, OE was an inflected or “synthetic” language with a well-developed system of morphological categories.



The time of the restoration of English to the position of the state and literary language and the time of literary flourishing. The time of the restoration of English to the position of the state and literary language and the time of literary flourishing. The main dialect used in writing and literature was the mixed dialect of London, which arose in the 14th c.


A time of progress in culture, education and literature. A time of progress in culture, education and literature. The formation of the national English language. A time of sweeping changes at all levels. The period of variety and free choice in pronunciation, vocabulary and grammar.

Establishment of “norms”, which were fixed as rules in the numerous dictionaries and grammar-books published at the time. Establishment of “norms”, which were fixed as rules in the numerous dictionaries and grammar-books published at the time. The 18th c. literary English differentiated into distinct styles. “Fixing the pronunciation”, and normalisation and restriction of word usage and grammatical construction.

By the 19th c. English had achieved the relative stability and had acquired all the properties of a national language, with its recognised standards. By the 19th c. English had achieved the relative stability and had acquired all the properties of a national language, with its recognised standards. The expansion of English overseas proceeded together with the growth of the British Empire in the 19th c.

The 20th c. witnessed considerable intermixture of dialects. The local dialects are being displaced by Standard English. The “best” form of English, the Received Standard, is being spread through new channels: the press, radio, cinema and television. The 20th c. witnessed considerable intermixture of dialects. The local dialects are being displaced by Standard English. The “best” form of English, the Received Standard, is being spread through new channels: the press, radio, cinema and television.


How many periods is the history of English traditionally divided into? What are they? What are their boundaries? How many periods is the history of English traditionally divided into? What are they? What are their boundaries? How many periods does Pr. Rastorguyeva subdivide the history of English language into? What do the following dates stand for: the 7th c.; 1475; the 5th c.; 1066; the 11th c. – the 15th c.; the 5th c. – the 11th c. Characterise the main periods in the history of English.

Основная учебная литература: Основная учебная литература: Расторгуева Т.А. История английского языка: Учебник для вузов М.: Астрель, 2003 (чз-5, аб-15). Иванова И., Чахоян Л., Беляева Т. История английского языка: Учебник. Хрестоматия. Словарь/ И.Иванова, Л.Чахоян,Т.Беляева СПб.: Лань, 2006 (чз-5, аб-17). Дополнительная учебная литература: Ярцева В.Н. Языкознание: Большой энциклопедический словарь / Под ред. В.Н.Ярцевой М.: Большая Российская энциклопедия, 2000 (чз-3). «Сrosscultural Aspects of The English Language History (Historical, social and cultural backgrounds of the English language history)»: учебное пособие по курсу истории английского языка/ Сост.: Р.Ж. Саурбаев, C.Г. Кулагина; Сургут. гос ун-т. – Сургут: Изд-во СурГУ, 2003 (медиатека ИнЕУ).































