Презентация на тему: Conditionals - Type 0/Type 1

Conditionals - Type 0/Type 1

•A conditional consists of two parts: the if –clause ( hypothesis), which begins with the word if, and the main clause, which shows the result of the hypothesis.f.E.If-clause-If you come early, -we’ll stay longer. - main clause

•When the if- clause comes before the main clause, we separate them with a comma. When the, main clause comes before the if-clause ,then we do not separate them with a comma.

Conditional Type 0Use•Conditional Type 0 express a general truth, a law of nature, something which is always true or something that always happens as a result of something else.If you heat water, it boils.If you put salt on ice, it melts.

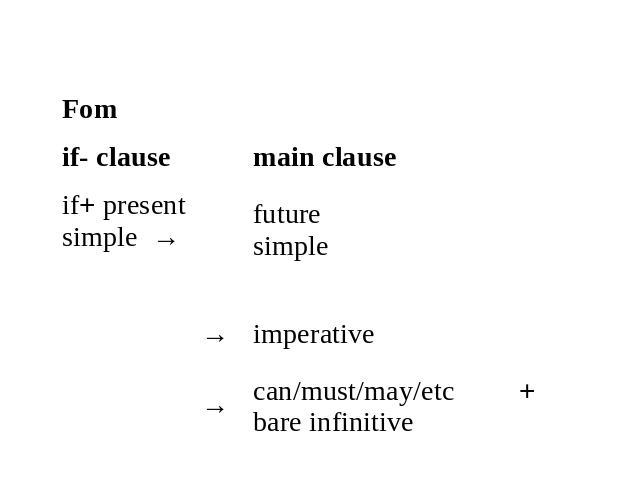
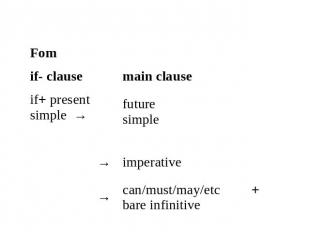
If/When you boil water, it makes steam.• In this type of conditional we can use when instead of if.Form

• Conditionals Type 1 express a real or very probable situation in the present or futureUse Conditional Type 1

Unless you like those trousers, I'll buy them.If you don't like those trousers, I'll buy them.We can use unless instead of if … not in the if-clause. The verb after unless is always in the affirmative

Relatives (who/ which/ whose/ where/ that) • Relative pronouns (who/ which/ whose/ where/ that) introduce relative clauses. We use relative clauses to identify/describe the person or thing in the main clause. The man who is wearing a black coat /relative clause/ is the manager of the bank.

• We use who/ that instead of subject pronouns (I, you, he, etc) to refer to people. The man who/ that robbed the bank was caught by the police.• We use which/ that to refer to objects or animals. The table which/ that is in the kitchen is very old.

• We use whose instead of possessive adjectives (my, your, his, etc) with people , objects and animals to show possession. That’s the woman whose handbag was stolen.• We use where (relative adverb) to refer to place.A hospital is a place where people go when they are ill.