Презентация на тему: The skeleton

Independent work of students of English The skeletonPrepared by:, 09-022 OMChecked by: Totanova NazgulAlmaty 2010

Skeletal System - Functions Support & shape to bodyProtection of internal organsMovement in union with musclesStorage of minerals (calcium, phosphorus) & lipidsBlood cell production

The Skeletal System Know the Skeletal AnatomyAxial SkeletonAppendicular SkeletonSurface Anatomy of the boneBy x-ray or diagramStructure/function of joints, muscle and ligament attachments Including range of motion
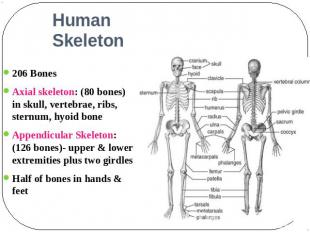
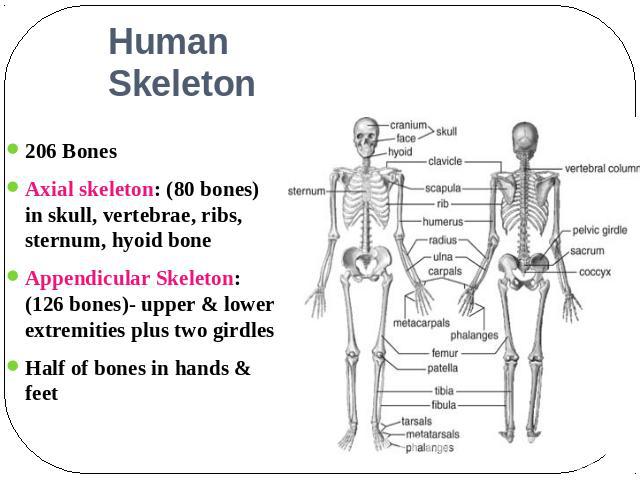
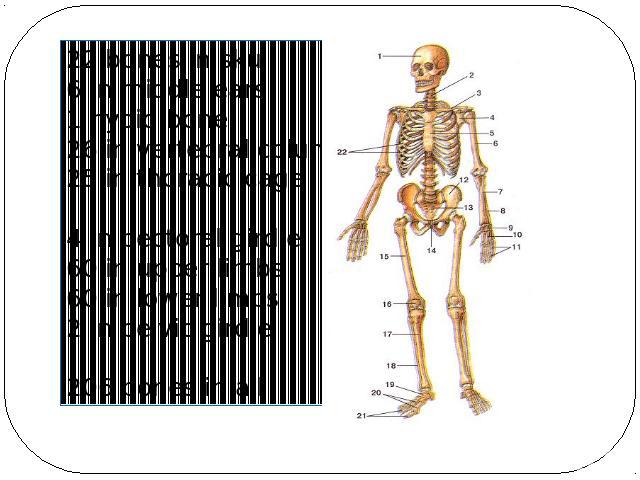
Human Skeleton 206 BonesAxial skeleton: (80 bones) in skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, hyoid bone Appendicular Skeleton: (126 bones)- upper & lower extremities plus two girdles Half of bones in hands & feet
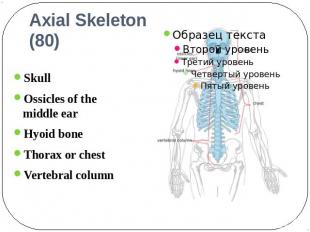
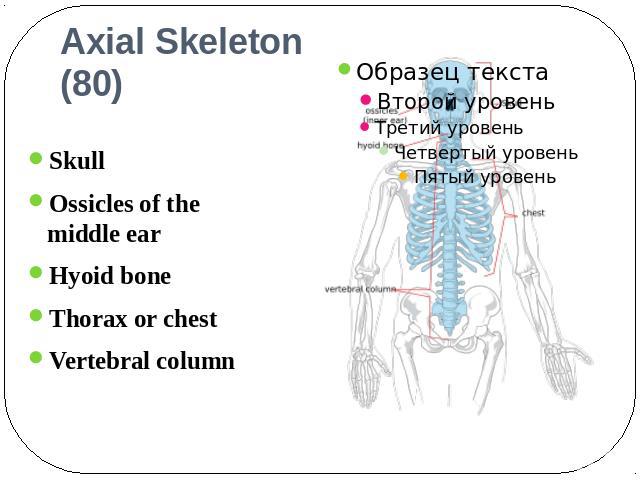
Axial Skeleton (80) Skull Ossicles of the middle earHyoid bone Thorax or chest Vertebral column
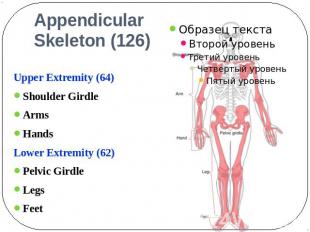
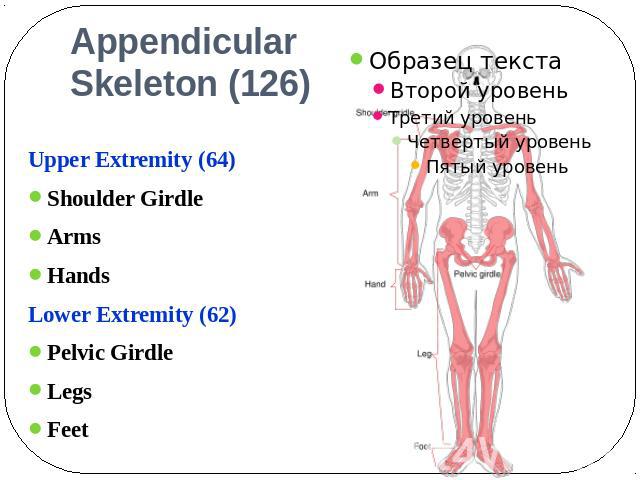
AppendicularSkeleton (126) Upper Extremity (64)Shoulder GirdleArmsHandsLower Extremity (62)Pelvic GirdleLegsFeet
Types of Bone Long bones: longer than they are wide; shaft & 2 ends (e.g.: bones of arms & legs,except wrist, ankle & patella)Short bones: roughly cube-shaped (e.g.: ankle & wrist bones)Sesamoid bones: short bones within tendons (e.g.: patella)Flat bones: thin, flat & often curved (e.g.,: sternum, scapulae, ribs & most skullbones)Irregular bones: odd shapes; don't fit into other classes (e.g.: hip bones & vertebrae)
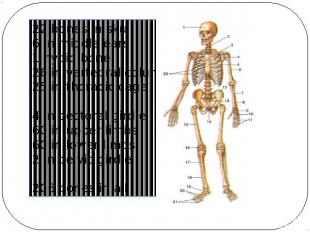
22 bones in skull6 in middle ears1 hyoid bone26 in vertebral column25 in thoracic cage4 in pectoral girdle60 in upper limbs60 in lower limbs2 in pelvic girdle206 bones in all
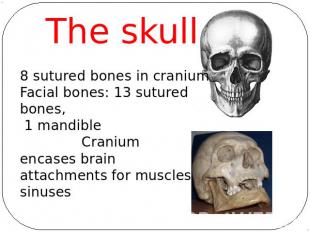
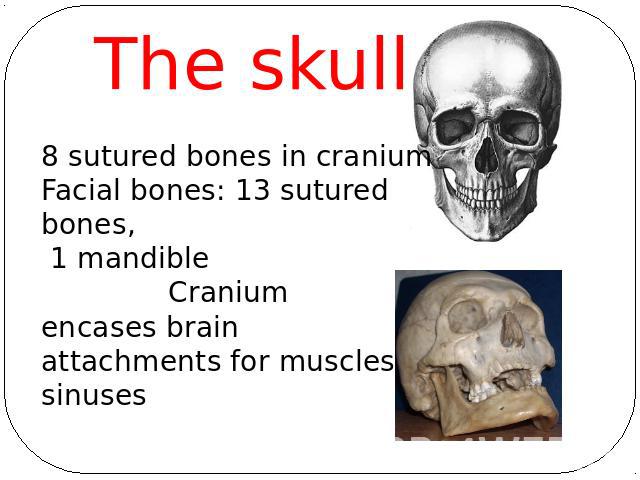
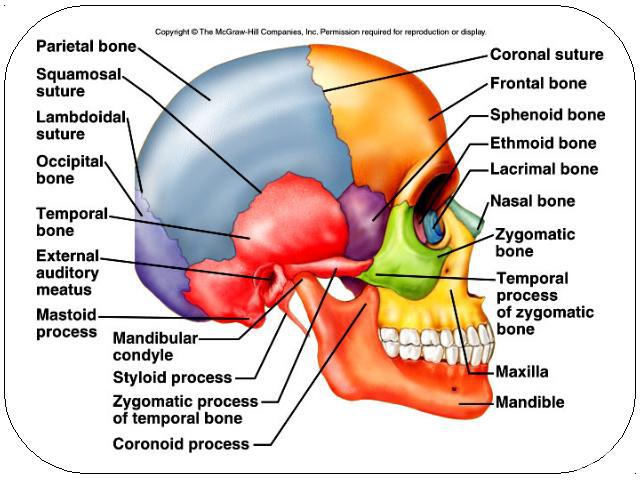
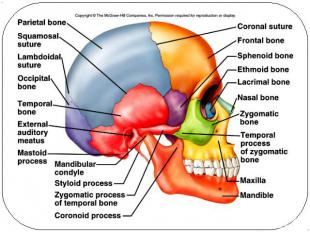
The skull8 sutured bones in craniumFacial bones: 13 sutured bones, 1 mandible Craniumencases brainattachments for musclessinuses

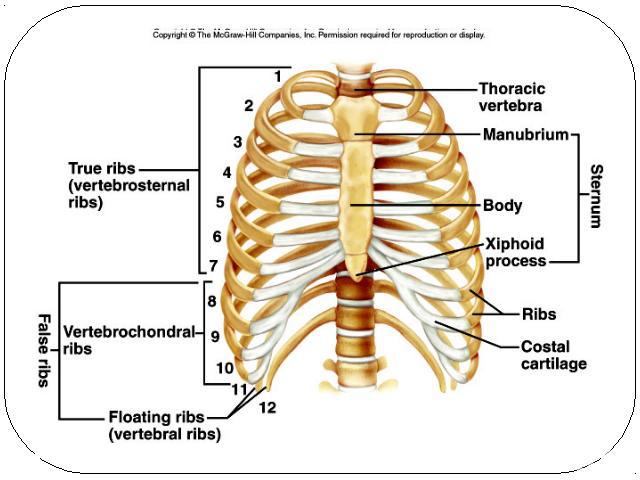
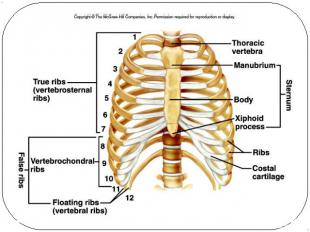
Thoracic cage ribs thoracic vertebrae sternum costal cartilages True ribs are directly attached to the sternum (first seven pairs) Three false ribs are joined to the 7th ribTwo pairs of floating ribs

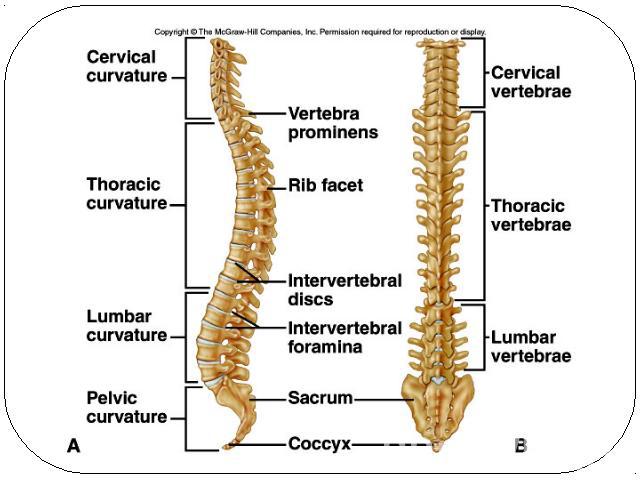
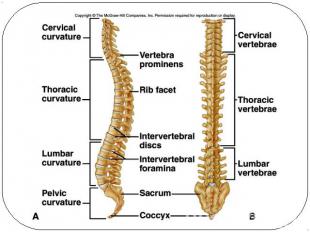
Vertebral column 7 cervial vertebrae 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 1 sacrum (5 fused) 1 coccyx (4 fused)Vertebrae vary in size and morphology
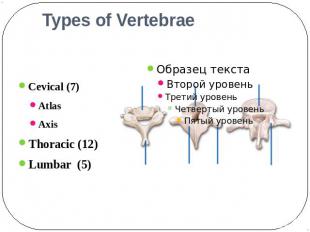
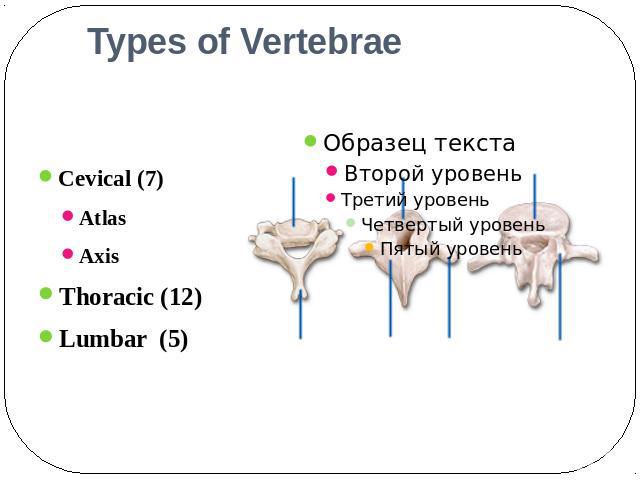
Types of Vertebrae Cevical (7)AtlasAxis Thoracic (12)Lumbar (5)

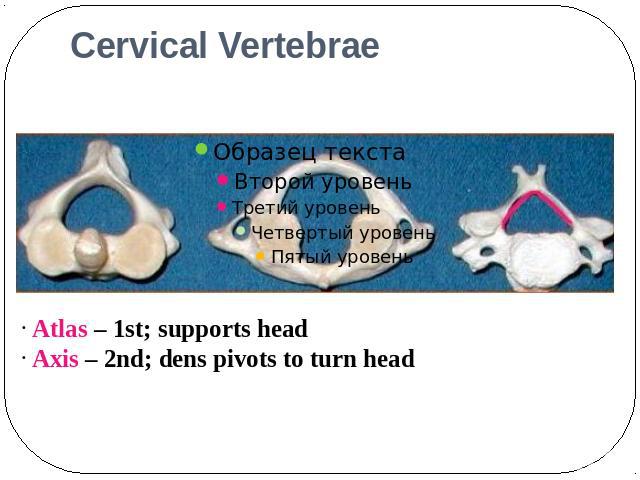
Cervical Vertebrae Atlas – 1st; supports head Axis – 2nd; dens pivots to turn head
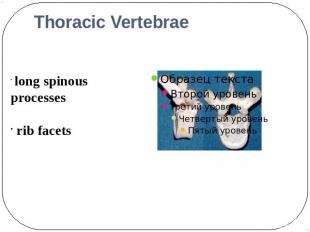
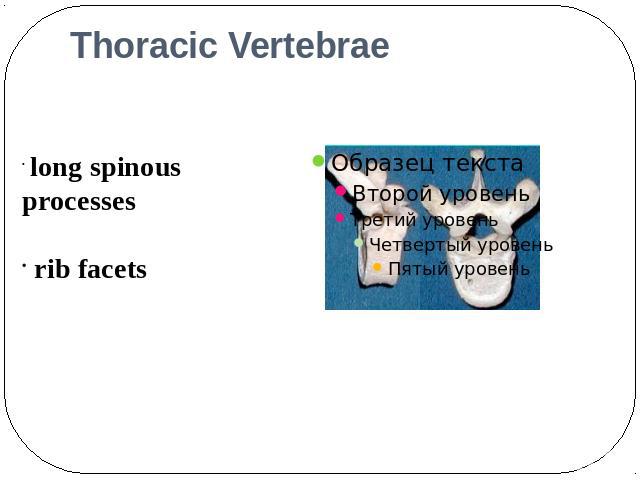
Thoracic Vertebrae long spinousprocesses rib facets
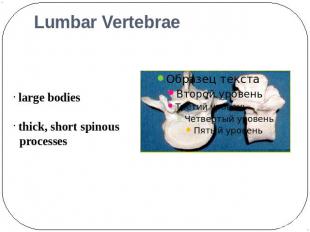
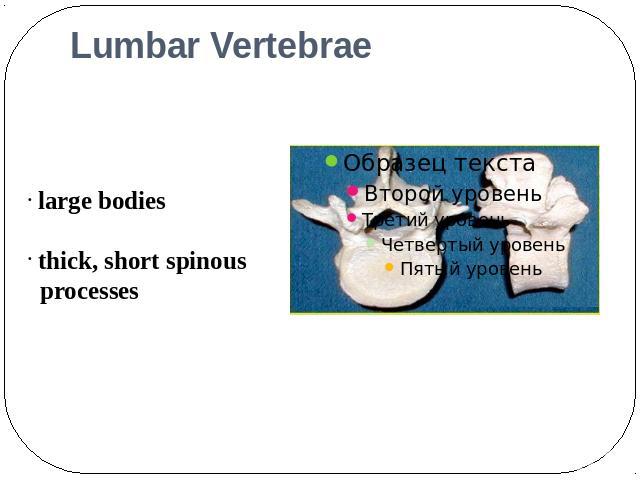
Lumbar Vertebrae large bodies thick, short spinous processes

Bone Cells Osteoblasts – bone forming cells synthesize and secrete unmineralized ground substance and are found in areas of high metabolism within the bone Osteocytes – mature bone cells made from osteoblasts that have made bone tissue around themselves. They maintain healthy bone tissue by secreting enzymes and controlling the bone mineral content; they also control the calcium release from the bone tissue to the blood. Osteogenic cells respond to traumas, such as fractures, by giving rise to bone-forming cells and bone-destroying cells Osteoclasts – bone absorbing cell – large cells that break down bone tissue – important to growth, healing, remodeling Bone lining cells - made from osteoblasts along the surface of most bones in an adult. Bone-lining cells are thought to regulate the movement of calcium and phosphate into and out of the bone
Types of Skeletal Cartilage Hyaline Cartilages: fine collagen fiber matrix- most abundant type- found in articular (movable joint) cartilages, costal cartilages (connect ribs tosternum), respiratory cartilages (in larynx & upper respiratory passageways) & nasal cartilagesElastic Cartilages: similar to hyaline cartilage, more elastic fibers (very flexible) – found in external ear & epiglottis (larynx covering)Fibrocartilage: rows of chondrocytes with thick collagen fibers; highly compressible with great tensile strength- found in menisci of knee, intervertebral discs & pubic symphysis