Презентация на тему: The Siege of Leningrad

Presentation on "The Siege of Leningrad". Fulfilled: student class 9b Shahova Asma.

The Siege of Leningrad - a military blockade . Lasted from September 8, 1941 to January 27, 1944 (the blockade ring was broken January 18, 1943) - 872 days. By the beginning of the blockade of the city did not have enough in terms of food supplies and fuel. The only way communication with Leningrad remained Ladoga, is within the reach of artillery besiegers. As a result, started in Leningrad famine, made worse by the harsh winter of the blockade first, problems with heating and transport, has led to hundreds of thousands of deaths among residents.

Plan Barbarossa The capture of Leningrad was part of a plan developed by Nazi Germany war against the Soviet Union - a plan "Barbarossa". It provided that the Soviet Union must be completely destroyed within 3-4 months of the summer and autumn of 1941, that is, in a lightning war ("Blitzkrieg"). By November 1941, German troops were to capture the entire European part of the USSR. According to the plan "Ost" ("East") was assumed for years to destroy large parts of the Soviet Union, primarily Russian, Ukrainians and Belarusians, and all Jews and gypsies - all at least 30 million people. None of the people inhabiting the Soviet Union, should not have the right to statehood or autonomy.

Soviet-Finnish war 1941-1944 years Starting from June 21, 1941 Finland started to conduct military operations against the Soviet Union. June 29, 1941 Finnish troops by clicking the border, began ground operation against the USSR.

Output forces opponents to Leningrad In the first 18 days of the onset of the 4th Panzer Group fought the enemy was more than 600 kilometers. July 5-6, enemy troops occupied the city, and on July 9 - Pskov, located 280 kilometers from Leningrad. From Pskov, the shortest way is to Leningrad to Kiev highway, going through the Meadow. Luga defense line was well prepared in engineering terms: fortifications were built 175 kilometers long and a total depth of 10-15 kilometers. Defenses built by the citizens of Leningrad, most of them women and children (the men went into the army and militia).In Luga fortified area was delayed the German advance. Dispatches a team of German troops to headquarters: Panzer Group Hoepner, Vanguard is exhausted and tired, only slightly advanced toward Leningrad . Hepner offensive stopped ... Russian fighting, as always, with great ferocity. Only in 1941, has built more than 700 tanks left in the city. During the same time it was released 480 armored vehicles and 58 armored trains, often armed with powerful naval guns. At Rzhev artillery range combat capability was found naval guns caliber 406 mm. August 14-15, the Germans managed to break through the wetland, June 29, crossed the border, the Finnish army began fighting on the Karelian Isthmus. July 31 launched a major offensive in the direction of the Finnish Leningrad. By early September, the Finns went existed prior to the signing of a peace treaty in 1940 the old Soviet-Finnish border September 6, 1941, Hitler issued an order stopping the offensive forces of the "North" in Leningrad, have already reached the suburbs of the city, and gives orders to Marshal Leeb Heppner give all the tanks and a significant number of troops in order to "as soon as possible" to launch an attack on Moscow. In this situation, Hitler actually imagined the huge losses it would suffer by joining the urban fighting, its decision condemned its population to starvation.

The German attack on the Soviet Union and Finland.

Leningrad defensive operation In late August 1941, the German offensive was resumed. German troops broke through the defensive line Luga and headed to Leningrad. September 8 enemy reached the Lake Ladoga, captured Shlisselburg, taking control of the source of the Neva, and blockaded Leningrad from the land. This day is considered the beginning of the siege. Severed all rail, river and road communications.

Soldiers defending Leningrad these days, were killed. Leeb continued success on the nearest approaches to the city. In the end, the enemy stopped at 4-7 km from the city, in fact, in the suburbs. Despite the proximity of the front, Kirov Plant stop working throughout the siege. From the factory to the front line even went tram. It was the usual tram from the city center to the suburbs, but now it is used to transport troops and ammunition.

Change in tactics of war Battles of Leningrad did not stop, but changed their character. German troops began the destruction of heavy artillery shelling and bombing. Particularly strong were bombing and artillery strikes in October - November 1941. The Germans dropped on Leningrad thousands of incendiary bombs to cause massive fires. However, contrary to popular belief, the bombing could not be the main cause of the ensuing food crisis, as Leningrad, as any other metropolis, is equipped with "wheels", and food stocks destroyed, along with warehouses, the city would be enough for only a few days . So, hunger has become the most important factor determining the fate of the population of Leningrad. Blockade imposed by the German army, was deliberately aimed at the extinction of the urban population.

The winter of 1941-1942 November 20 - the fifth time the population and for the third time troops - had to reduce the bread ration standards. Soldiers on the front line began to receive 500 grams a day, the workers - 250 grams, employees, dependents and soldiers, are not on the front line - 125 grams. And except for the bread, almost nothing. In besieged Leningrad famine. Workers - 250 grams of bread per day, Employees, dependents and children up to 12 years - 125 grams Paramilitary security personnel, firefighters, fighter units, vocational schools and schools FZO, who was on the boiler allowance - 300 grams The troops of the first line - 500 grams. Card at the time of the siege of Leningrad bread

The deteriorating situation in the city. In November 1941, the situation deteriorated citizens. Deaths from starvation became widespread. Special funeral service daily in the streets picked up only about a hundred corpses. The number of victims of hunger was growing rapidly - every day in Leningrad died more than 4,000 people, which is a hundred times greater than the rate of fatalities in peacetime. There were days when he died 6-7 thousand people. Only in December, 52,881 people died, a loss in January-February - 199 187 people. Male mortality significantly higher than women - for every 100 deaths had an average of 63 men and 37 women. By the end of the war, women made up the bulk of the urban population.

Reducing street deaths. In the spring of 1942, due to the warming and better nutrition, significantly reduced the number of sudden deaths in the streets. Thus, in February, the streets were picked up about 7,000 corpses, in April - about 600, and in May - 50 corpses. In March 1942, all able-bodied citizens came out to clear the city of garbage. In April-May 1942, there was a further improvement in the living conditions of the population: the restoration of utilities. Resumed operations of many companies.
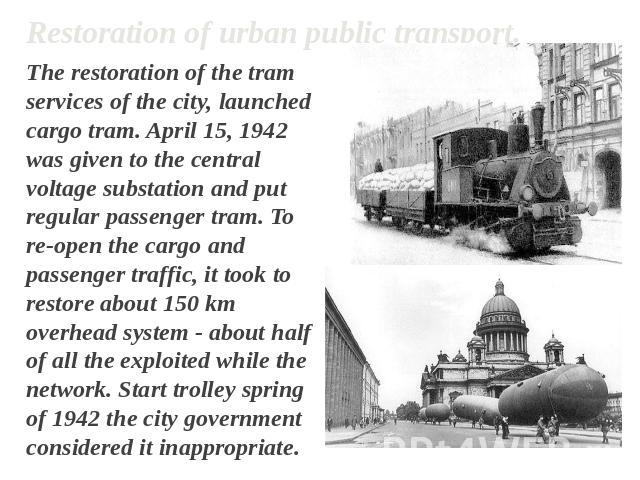
Restoration of urban public transport. The restoration of the tram services of the city, launched cargo tram. April 15, 1942 was given to the central voltage substation and put regular passenger tram. To re-open the cargo and passenger traffic, it took to restore about 150 km overhead system - about half of all the exploited while the network. Start trolley spring of 1942 the city government considered it inappropriate.

1944.Complete liberation of Leningrad from the enemy blockade. January 20, Soviet troops have made significant progress: the Leningrad Front defeated Krasnoselsk-Ropshinsk enemy forces, and parts of the Volkhov Front liberated Novgorod. This allowed 21 January Govorov and AA Zhdanov appeal to Stalin: Due to the complete liberation of Leningrad from the enemy blockade and the shelling of the enemy please allow: 1. Publish and post on this order to the troops of the front. 2. In honor of the victory, produce in Leningrad January 27 c / g at 20.00 hours salute of twenty-four artillery salvoes of three hundred and twenty-four guns. Stalin approved a request from the command of the Leningrad front and 27 January in Leningrad was produced fireworks in honor of the final liberation of the city from the siege, which lasted 872 days.

Results of the blockade. Over the years of blockade were killed, according to various estimates, from 300,000 to 1.5 million. So, at the Nuremberg trials featured the number 632 000 people. Only 3% of them died from the bombing and shelling, and the remaining 97% died of hunger. Most died in the siege of Leningrad residents buried at Memorial Cemetery Piskaryovskoye in the Vyborg. In a long line of graves lie the victims of the blockade, which number only in this cemetery is 640 000 people died of starvation, and more than 17,000 people who have been victims of air raids and artillery shelling. The total number of civilian deaths in the city during the war more than 1.2 million people.

In the park built a chapel and a monument to the "trolley" - one of the worst sites of St. Petersburg. At these trolleys were taken to the nearby quarry after burning in furnaces of the plant remains of the dead.

Monuments of the defense of Leningrad. One of the monuments "Rzhev corridor" on the road of the Revolution

Piskariovskoye Memorial Cemetery Rotunda in Spb victory park