Презентация на тему: The historyof the english language

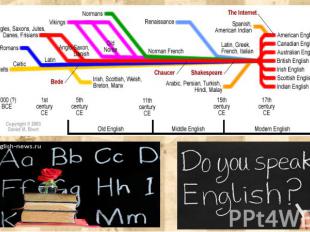

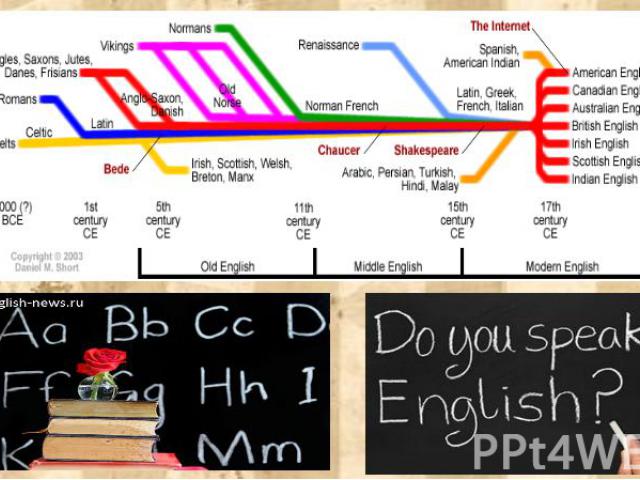
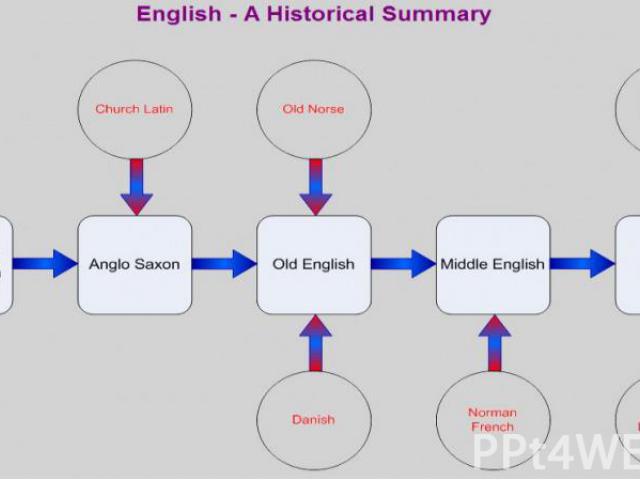
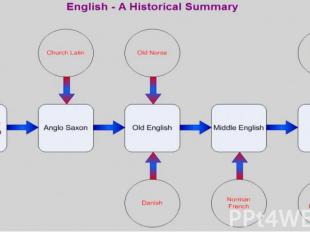
Periods in the history of English The history of English covers roughly 1200 years. Traditional divides English history into three periods: The Old English period begins about 700 a. d. and lasts till about 12th century. The Middle English period lasts from about the beginning of the 12th century till 15th century. The Modern English period begins at about 15th century and lasts to the present day.

The ultimate origins of English lie in Indo-European , a family of languages consisting of most of the languages of Europe as well as those of Iran, the Indian subcontinent, and other parts of Asia. Because little is known about ancient Indo-European we'll begin our survey in Britain in the first century AD The ultimate origins of English lie in Indo-European , a family of languages consisting of most of the languages of Europe as well as those of Iran, the Indian subcontinent, and other parts of Asia. Because little is known about ancient Indo-European we'll begin our survey in Britain in the first century AD


Romans 43 AD The Romans invade Britain, beginning 400 AD years of control over much of the island. Early 5th century with the collapse of the empire, Romans withdraw from Britain. So many words have Latin roots in modern English. For example, word “castra” (camp) meets in words -Lancaster, Manchester, Leicester. Many of the most commonly used words in modern English have Latin roots, for example: words street, wall, wine, pear, pepper.

500-1100: The Old English (or Anglo-Saxon) Period