Презентация на тему: The Czech Republic

The Czech Republic

GEOGRAFICAL POSITION The country has borders with Poland to the north, Germany to the northwest and southwest, Austria to the south, and Slovakia to the east. Bohemia to the west consists of a basinand the Vltava riverandmostly low mountains such as the Krkonoše range. The highest point in the country, Sněžka, at 1,602 m, is located here. Moravia, the eastern part of the country, is also quite hilly. It is drained mainly by the Morava RiverWater from the landlocked Czech Republic flows to three different seas: the North Sea, Baltic Sea and Black Sea. Area 78,866 km²

THE LANDSCAPE OF THE COUNTRY The landscape of the northern regions is typically hilly, wooded. To the east and south of the country there are plains. THE BOHEMIAN HILLS The Hills are situated in northern Bohemia along both banks of lower stream of Czech part of Elbe. Typical conical hills are result of Tertiary Formation volcanic activity. THE WHITE CARPATHIAN MOUNTAINS The Mountains are situated in southeast part of Czech Republic. The mountain range begins at Zarieči in Slovakia. The archaeological monument of the country is the South Bohemian landscape of lakes and pools, and the lost landscape of the Rozmberk enclosures around the town of Netolice.

The Protected landscape areas The First zone contains natural and semi-natural forest communities, virtually untouched by man, and most valuable varied non-forest lands.Care of the zone focuses on fine forms of forest management.This zone, the most strict, includes specially protected areas of smaller sizes - the so-called small-scale areas. The Second zone includes forest crops with more significantly changed species composed of pro-nature forest communities. Natural recovery is preferred in forest management; meadows and pastures should be treated delicately. The Third zone includes cultivated farmlands, meadows, pastures, scattered built-up areas and rich representations of non-forest wooded areas. This zone allows for the placement of residential and business activities, together with more intense agricultural production.

Agriculture Czech agriculture has a hundred-years proof tradition which has brought fame to the country abroad. Especially milk, life animals, cereals, sugar and malt dominate the agrarian export in long term. Agricultural developments in the Czech Republic since 1989Agriculture used to be one of the most preferred branches in the central directive system of the Czech Republic. The switch to a market economy meant significant pressure on adaptation of agriculture to new economic conditions and sales opportunities in terms of farms' structure and capacity. The total area of agricultural land resources of the Czech Republic is 4,269 thousand hectares.

The features of Czech agriculture The value of animal husbandry slightly prevails above vegetable production, but the share of vegetable production has increased a bit in the past 10 years. The structure of vegetable production changed because of a drop in the production of grain, potatoes and mainly white beet. At the end of 2004, Czech agriculture had 678 farmer cooperatives, 2,319 trade companies, 32,231 individuals' companies and 180 other entities in operation.

THE PROBLEMS Agriculture makes up the smallest sector in the Czech economy, contributing about 5 percent of the total incomes. The primary agricultural products are sugar beets, fodder roots for animal feed, potatoes, wheat, hops, fruit, pigs, cattle, poultry, and forest products.Under the communist economic system, Czech agriculture was collectivized, meaning that small private farms were taken by the government in order to create state-owned cooperatives. After the end of communism in 1989, these cooperatives were transferred to private owners, often by the direct sale of the farm as a unit.
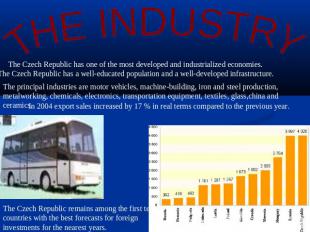
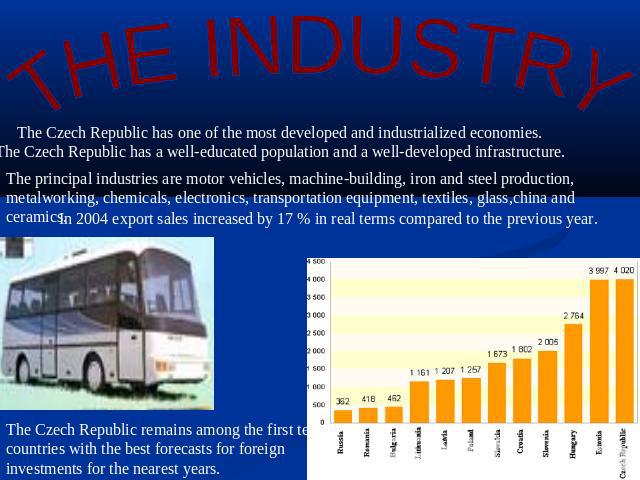
THE INDUSTRY The Czech Republic has one of the most developed and industrialized economies. The Czech Republic has a well-educated population and a well-developed infrastructure. The principal industries are motor vehicles, machine-building, iron and steel production, metalworking, chemicals, electronics, transportation equipment, textiles, glass,china and ceramics.In 2004 export sales increased by 17 % in real terms compared to the previous year. The Czech Republic remains among the first ten countries with the best forecasts for foreign investments for the nearest years.

THE FIELDS OF THE INDUSTRY