Презентация на тему: Talking About Writing


Writing, as a discipline, has its own terminology and jargon which includes the following: Writing, as a discipline, has its own terminology and jargon which includes the following:
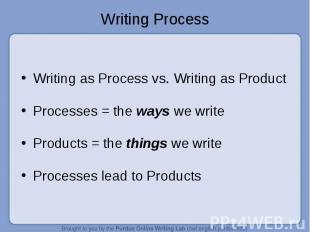
Writing as Process vs. Writing as Product Processes = the ways we write Products = the things we write Processes lead to Products

“Draft” = a completed version of a project “Draft” = a completed version of a project Typically, subsequent “drafts” of written assignments do not add anything major to each new version Each draft represents efforts at refining an already completed project, NOT adding new sections of material

Prewriting / Invention = all the activities a writer does before writing any draft of a written assignment Prewriting / Invention = all the activities a writer does before writing any draft of a written assignment These activities could include: Brainstorming Research Outlining Summarizing main ideas Making a diagram or other schematic.

Thesis Statement = The main idea or main point of a written assignment. Thesis Statement = The main idea or main point of a written assignment. It is specific It often appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper It can be modified to reflect what actually ended up being discussed in the paper

“Introduction” = the broad beginning of a written assignment “Introduction” = the broad beginning of a written assignment It should answer these questions: What is this paper about? Why am I reading it? What do you want me to do? It should set the context for the paper It should state why the main idea is important A thesis statement is typically placed at the end of an introduction
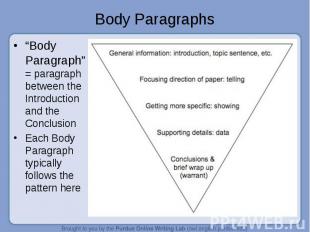
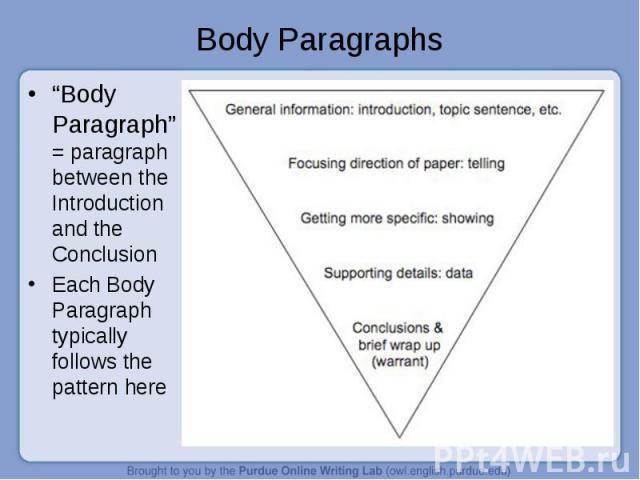
“Body Paragraph” = paragraph between the Introduction and the Conclusion “Body Paragraph” = paragraph between the Introduction and the Conclusion Each Body Paragraph typically follows the pattern here

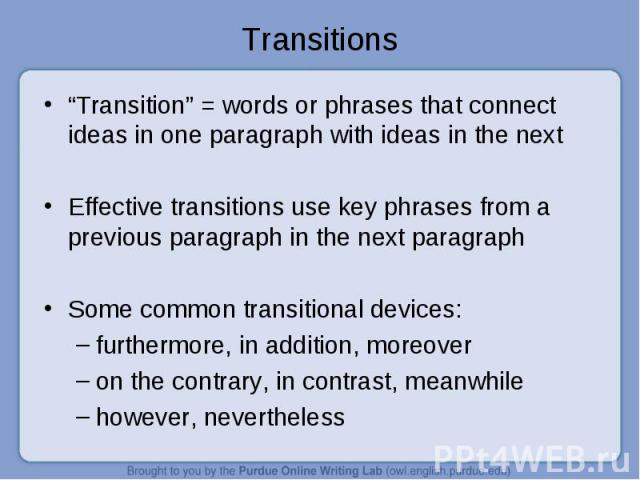
“Transition” = words or phrases that connect ideas in one paragraph with ideas in the next “Transition” = words or phrases that connect ideas in one paragraph with ideas in the next Effective transitions use key phrases from a previous paragraph in the next paragraph Some common transitional devices: furthermore, in addition, moreover on the contrary, in contrast, meanwhile however, nevertheless

“Conclusion” = the end parts written assignments that wrap up what authors have been discussing in their papers “Conclusion” = the end parts written assignments that wrap up what authors have been discussing in their papers Conclusions could Restate the topic and its importance Restate the thesis statement Resolve opposing viewpoints Include a call for action Overview future research possibilities

“Revision” = any beneficial change to a paper from one draft to another Generally, “revision” means larger changes with structure or content “Proofreading” = means only revising to correct spelling or grammatical errors

“Citations” = the methods writers use to reference the sources they quote Modern Language Association (MLA): Purdue OWL: http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/01/ American Psychological Association (APA): Purdue OWL: http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/01/ Chicago Manual of Style (CMS): Purdue OWL: http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/01/

“Primary Research” = any type of research you go out and collect yourself “Secondary Research” = every other kind of research

For more OWL resources, see the following: For more OWL resources, see the following: Essay Writing Prewriting (Invention) Creating a Thesis Statement Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for Argument Papers Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for Exploratory Papers Transitions and Transitional Devices Proofreading Paramedic Method Reverse Paramedic Method MLA 2009 Formatting and Style Guide APA Formatting and Style Guide Chicago Manual of Style Conducting Primary Research